Set Mosaic Dataset Properties
How to Set Mosaic Dataset Properties Tool in Arc Toolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??
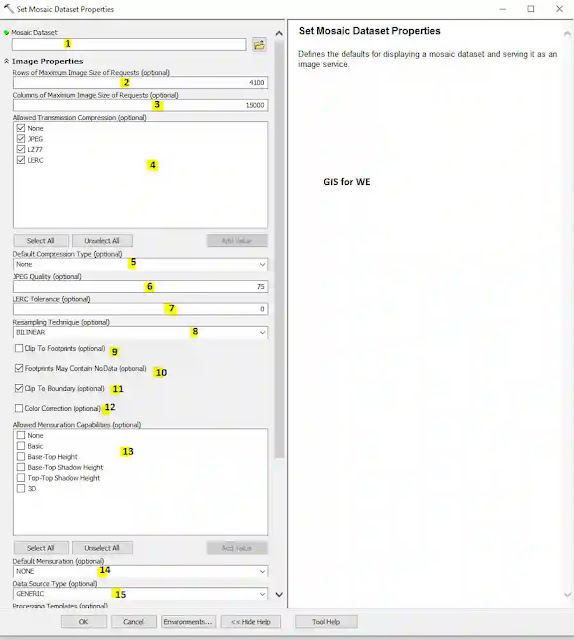 |
| Set Mosaic Dataset Properties |
Path to access the tool
:
Set Mosaic Dataset Properties Tool, Mosaic Dataset Toolset, Raster Box, Data Management Tools Toolbox
Set Mosaic Dataset Properties
Defines the defaults for displaying a mosaic dataset and serving it as an image service.
1. Mosaic Dataset
The mosaic dataset whose properties need to be set.
2. Rows of Maximum Image Size of Requests (optional)
The maximum number of rows for the mosaicked image, generated by the mosaic dataset for each request. This can help control how much work your server has to do when clients see your imagery. A higher number will create a larger image, but will also increase the amount of time to process the mosaic dataset. It is possible to set the value too small, and the image may not display.
3. Columns of Maximum Image Size of Requests (optional)
The maximum number of columns for the mosaicked image, generated by the mosaic dataset for each request. This can help control how much work your server has to do when clients see your imagery. A higher number will create a larger image, but will also increase the amount of time to process the mosaic dataset. It is possible to set the value too small, and the image may not display.
4. Allowed Transmission Compression (optional)
Define the method of compression for transmitting the mosaicked image from the computer to the display (or from the server to the client).
- None—No compression will be used.
- JPEG— Compresses up to 8:1 and is suitable for backdrops
- LZ77— Compresses approximately 2:1. Suitable for analysis.
- LERC—Compresses between 10:1 and 20:1. Compresses fast and is suitable for serving raw imagery with high bit-depth (12-bit to 32-bit)
5. Default Compression Type (optional)
Set the default compression type. The default compression must be in the Allowed Transmission Compression list or already set in the mosaic dataset's Allowed Compression Methods property.
- None—No compression will be used.
- JPEG— Compresses up to 8:1 and is suitable for backdrops
- LZ77— Compresses approximately 2:1. Suitable for analysis.
- LERC—Compresses between 10:1 and 20:1. Compresses fast and is suitable for serving raw imagery with high bit-depth (12-bit to 32-bit)
6. JPEG Quality (optional)
The compression quality when using JPEG. Compression quality ranges from 1 to 100. A higher number means better image quality but less compression.
7. LERC Tolerance (optional)
Limits the per pixel error when using LERC compression. This value is specified in the units of the mosaic dataset. For example, if the error is 10 centimeters and the mosaic dataset is in meters, enter 0.1.
8. Resampling Technique (optional)
Determines how pixel values will be calculated when the dataset is displayed at small scales. Choose an appropriate technique based on the type of data you have.
- NEAREST—The fastest resampling method, and it minimizes changes to pixel values. Suitable for discrete data, such as land cover.
- BILINEAR— Calculates the value of each pixel by averaging, based on distance, the values of the surrounding 4 pixels. Suitable for continuous data.
- CUBIC—Calculates the value of each pixel by fitting a smooth curve based on the surrounding 16 pixels. Produces the smoothest image, but can create values outside of the range found in the source data. Suitable for continuous data.
- MAJORITY—Determines the value of each pixel based on the most popular value within a 3 by 3 window. Suitable for discrete data.
9. Clip To Footprints (optional)
Often the raster dataset and its footprint have the same extent. If they differ, you can clip the raster dataset to the footprint.
- Unchecked—Do not clip the rasters to the footprint. This is the default.
- Checked—Clip the rasters to the footprint.
10. Footprints May Contain NoData (optional)
Allow for pixels that have NoData values.
- Checked—Show pixels with NoData values.
- Unchecked—Do not show pixels with NoData values. Note that while you may see an improvement in performance, if your imagery does have NoData values, they will appear as holes in your mosaic dataset.
11. Clip To Boundary (optional)
Often the mosaic dataset and its boundary have the same extent. If they differ, you can clip the mosaic dataset to the boundary.
- Checked—Clip the mosaicked image to the boundary. This is the default.
- Unchecked—Do not clip the mosaicked image to the boundary.
12. Color Correction (optional)
Enable color correction on the mosaic dataset.
- Unchecked—Keep color correction off. This is the default.
- Checked—Use the color correction that has been set up for the mosaic dataset.
13. Allowed Mensuration Capabilities (optional)
Choose which measurements your viewers can perform on the mosaic dataset. The ability to perform vertical measurements is dependent on your imagery and may require a DEM.
- None—No mensuration capabilities will be allowed.
- Basic— Allow ground measurements such as distance, point, centroid, and area calculations.
- Base-Top Height—Allow measurements from the base to the top of features. Rational polynomial coefficients must be imbedded within the imagery.
- Base-Top Shadow Height—Allow measurements from the base of a feature to the top of its shadow. Sun azimuth and sun elevation information is required.
- Top-Top Shadow Height—Allow measurements from the top of a feature to the top of its shadow. Sun azimuth, sun elevation, and rational polynomial coefficients are required.
- 3D—A DEM must be available.
15. Data Source Type (optional)
Define the type of imagery in the mosaic dataset.
- GENERIC—The mosaic dataset does not have a specified data type.
- THEMATIC—Thematic data has discrete values, such as land cover.
- PROCESSED—The mosaic dataset has been color adjusted.
- ELEVATION—The mosaic dataset contains elevation data.
- SCIENTIFIC—The mosaic dataset contains scientific data.
- VECTOR_UV—The mosaic dataset has two variables.
- VECTOR_MAGDIR—The mosaic dataset has magnitude and direction.
Processing Templates
(optional)
Choose the function chains that you want to use to process a mosaic dataset
or the mosaic dataset items, on-the-fly. You can add, remove, or reorder the
function chains.
All the template names that are added need to be unique.
Default Processing
Template (optional)
Define the default function chain. The default function chain will be applied
when the mosaic dataset is accessed.
Allowed Mosaic Methods
(optional)
Define the rules for displaying overlapping imagery.
- None—Order rasters based on the ObjectID in the mosaic dataset attribute
table.
- Center—Display imagery that is closest to the center of the screen.
- NorthWest—Display imagery that is closest to the northwest corner of the
mosaic dataset boundary.
- LockRaster—Select specific raster datasets to display.
- ByAttribute—Display and prioritize imagery based on a field in from the
attribute table.
- Nadir—Display the rasters with viewing angles closest to zero.
- Viewpoint—Display imagery that is closest to a selected viewing angle.
- Seamline—Smooth transitions between images using seamlines.
Default Mosaic Methods
(optional)
Choose the mosaic method that you prefer your views use. The default must be
set in the Allowed Mosaic Methods parameter list or already set in the mosaic
dataset's Allowed Mosaic Methods property.
- None—Order rasters based on the ObjectID in the mosaic dataset attribute
table.
- Center—Display imagery that is closest to the center of the screen.
- NorthWest—Display imagery that is closest to the northwest corner of the
mosaic dataset boundary.
- LockRaster—Select specific raster datasets to display.
- ByAttribute—Display and prioritize imagery based on a field in from the
attribute table.
- Nadir—Display the rasters with viewing angles closest to zero.
- Viewpoint—Display imagery that is closest to a selected viewing angle.
- Seamline—Smooth transitions between images using seamlines.
Product Definition
(optional)
Select a template that is either specific to the type of imagery you are
working with or is generic. The generic options include the standard supported
raster sensor types as follows:
- NONE—No band ordering is specified for the mosaic dataset. This is the
default.
- NATURAL_COLOR_RGB—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset, with red, green, and blue
wavelength ranges. This is designed for natural color imagery.
- NATURAL_COLOR_RGBI—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset, with red, green, blue,
and near infrared wavelength ranges.
- VECTOR_FIELD_UV—Create a mosaic dataset displaying two variables.
- VECTOR_FIELD_MAGNITUDE_DIRECTION—Create a mosaic dataset displaying
magnitude and direction.
- FALSE_COLOR_IRG—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset, with near infrared, red, and
green wavelength ranges.
- DMCII_3BANDS—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset using the DMCii wavelength
ranges.
- DEIMOS2_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Deimos-2 wavelength
ranges.
- DUBAISAT-2_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the DubaiSat-2
wavelength ranges.
- FORMOSAT-2_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the FORMOSAT-2
wavelength ranges.
- GEOEYE-1_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the GeoEye-1 wavelength
ranges.
- GF-1 PMS_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Gaofen-1
Panchromatic Multispectral Sensor wavelength ranges.
- GF-1 WFV_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Gaofen-1 Wide Field
of View Sensor wavelength ranges.
- GF-2 PMS_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Gaofen-2
Panchromatic Multispectral Sensor wavelength ranges.
- GF-4 PMI_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Gaofen-4
panchromatic and multispectral wavelength ranges.
- HJ 1A/1B CCD_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Huan Jing-1 CCD
Multispectral or Hyperspectral Sensor wavelength ranges.
- IKONOS_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the IKONOS wavelength
ranges.
- JILIN-1_3BANDS—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset using the Jilin-1 wavelength
ranges.
- KOMPSAT-2_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the KOMPSAT-2
wavelength ranges.
- KOMPSAT-3_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the KOMPSAT-3
wavelength ranges.
- LANDSAT_6BANDS—Create a 6-band mosaic dataset using the Landsat 5 and 7
wavelength ranges from the TM and ETM+ sensors.
- LANDSAT_8BANDS—Create an 8-band mosaic dataset using the LANDSAT 8
wavelength ranges.
- LANDSAT_MSS_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Landsat
wavelength ranges from the MSS sensor.
- PLEIADES-1_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the PLEIADES-1
wavelength ranges.
- QUICKBIRD_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the QuickBird
wavelength ranges.
- RAPIDEYE_5BANDS—Create a 5-band mosaic dataset using the RapidEye wavelength
ranges.
- SENTINEL2_13BANDS—Create a 13-band mosaic dataset using the Sentinel 2 MSI
wavelength ranges.
- SKYSAT_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the SkySat-C MSI
wavelength ranges.
- SPOT-5_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the SPOT-5 wavelength
ranges.
- SPOT-6_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the SPOT-6 wavelength
ranges.
- SPOT-7_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the SPOT-7 wavelength
ranges.
- TH-01_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Tian Hui-1 wavelength
ranges.
- WORLDVIEW-2_8BANDS—Create an 8-band mosaic dataset using the WorldView-2
wavelength ranges.
- WORLDVIEW-3_8BANDS—Create an 8-band mosaic dataset using the WorldView-3
wavelength ranges.
- WORLDVIEW-4_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the WorldView-4
wavelength ranges.
- ZY1-02C PMS_3BANDS—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset using the ZiYuan-1
panchromatic/multispectral wavelength ranges.
- ZY3-CRESDA_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the ZiYuan-3 CRESDA
wavelength ranges.
- ZY3-SASMAC_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the ZiYuan-3 SASMAC
wavelength ranges.
- CUSTOM—Define the number of bands and the average wavelength for each band.
Product Band Definitions
(optional)
Edit Product Definition by adjusting the wavelength ranges, changing the
number of bands or the band order, and adding new bands.
Order Field
(optional)
Choose the default field to use when ordering rasters using the By Attribute
mosaic method. The list of fields is defined as those in the attribute table
that are of type metadata and are integer. This list can include, but is not
limited to:
- Name
- MinPS
- MaxPS
- LowPS
- HighPS
- Tag
- GroupName
- ProductName
- CenterX
- CenterY
- ZOrder
- Shape_Length
- Shape_Area
If your field is a numeric or date field, then the Order Base parameter needs
to be set.
This parameter is not needed if By Attribute is not an allowed mosaic
method.
Order Base
(optional)
Sort the rasters based on their difference from this value in the field
selected in the Order Field parameter.
If you are using a Date attribute, then it needs to be in one of the
following formats:
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm:ss.s
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm:ss
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm
- YYYY/MM/DD HH
- YYYY/MM/DD
- YYYY/MM
- YYYY
Sorting Order Ascending
(optional)
Sort ascending or descending.
- Checked—Sort ascending. This is the default setting.
- Unchecked—Sort descending.
Mosaic Operator
(optional)
Define rules for resolving overlapping pixels.
- FIRST—Display the first image within the attribute table.
- LAST—Display the last image within the attribute table.
- MIN—Display the lowest pixel values.
- MAX—Display the highest pixel values.
- MEAN—Use arithmetic mean to average overlapping pixels.
- BLEND—Use a distance weighted algorithm to average overlapping pixels.
- SUM—Add all of the overlapping pixel values.
Blend Width
(optional)
The number of pixels over which to apply the Blend Mosaic Operator.
View Point Spacing X
(optional)
When using the viewpoint mosaic method, you can horizontally shift the center
of the image using this parameter. The units are the same as the spatial
reference system.
View Point Spacing Y
(optional)
When using the viewpoint mosaic method, you can vertically shift the center
of the image using this parameter. The units are the same as the spatial
reference system.
Max
Number Per Mosaic (optional)
Set the maximum number of raster datasets that can be displayed at a given
time in a mosaic dataset.
Cell Size Tolerance
Factor (optional)
Consider images of similar spatial resolutions as having the same nominal
resolution. For example, with a factor of 0.1, all images with cell sizes within
10 percent of each other will be grouped together for tools and operations that
use cell sizes.
Output Cell Size
(optional)
Set the cell size of the mosaic dataset using an existing raster dataset or
specify its width (x) and height (y).
Metadata Level
(optional)
Set the level of metadata to expose from the server to a client when
publishing the mosaic dataset.
- FULL—Transmit metadata about processing applied at the mosaic dataset level
as well as metadata related to the individual raster datasets.
- NONE—No metadata will be exposed to the client.
- BASIC—Transmit metadata related to individual raster datasets, such as the
number of columns and rows, cell size, and spatial reference information.
Allowed Transmission
Field (optional)
Limit the fields in the attribute table that clients can view. By default,
the list includes:
- Name
- MinPS
- MaxPS
- LowPS
- HighPS
- Tag
- GroupName
- ProductName
- CenterX
- CenterY
- ZOrder
- Shape_Length
- Shape_Area
Use
Time (optional)
Enable animation through time on the mosaic dataset. If time is activated,
you need to specify the start and end fields, and the time format.
- Unchecked—The mosaic dataset will not be time aware. This is the default.
- Checked—The mosaic dataset will be time aware. This allows the client to use
the Time Slider.
Start Time Field
(optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the start time.
End
Time Field (optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the end time.
Time Format
(optional)
Select the format that represents time in the fields chosen above.
- YYYY—Year
- YYYYMM—Year and month
- YYYY/MM—Year and month
- YYYY-MM—Year and month
- YYYYMMDD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY/MM/DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY-MM-DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction of
seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
Geographic
Transformation (optional)
The geographic transformations to associate with this mosaic
dataset.
Max
Number of Download Items (optional)
Limit the number of raster datasets that can be downloaded per
request.
Max
Number of Records Returned (optional)
Limit the number of records that can be downloaded per request.
Minimum Pixel
Contribution (optional)
Set the minimum number of pixels required for a mosaic dataset item to be
considered significant enough to be used in the mosaic dataset. Because of
overlapping imagery, you may have an item that is displaying a small sliver of
its overall image. Skipping these mosaic dataset items will help the performance
of the mosaic dataset.
Time Interval
(optional)
Specify the duration that represents each time step interval. The time step
interval defines the granularity of the temporal data. The unit of time is
specified in the Time Interval Units parameter.
Time Interval Units
(optional)
Choose the appropriate units for your time interval.
- None—There is no time unit, or the units are unknown.
- Milliseconds—The time units are in milliseconds.
- Seconds—The time units are in seconds.
- Minutes—The time units are in minutes.
- Hours—The time units are in hours.
- Days—The time units are in days.
- Weeks—The time units are in weeks.
- Months—The time units are in months.
- Years—The time units are in years.
- Decades—The time units are in decades.
16. Processing Templates (optional)
Choose the function chains that you want to use to process a mosaic dataset
or the mosaic dataset items, on-the-fly. You can add, remove, or reorder the
function chains.
All the template names that are added need to be unique.
Default Processing
Template (optional)
Define the default function chain. The default function chain will be applied
when the mosaic dataset is accessed.
Allowed Mosaic Methods
(optional)
Define the rules for displaying overlapping imagery.
- None—Order rasters based on the ObjectID in the mosaic dataset attribute
table.
- Center—Display imagery that is closest to the center of the screen.
- NorthWest—Display imagery that is closest to the northwest corner of the
mosaic dataset boundary.
- LockRaster—Select specific raster datasets to display.
- ByAttribute—Display and prioritize imagery based on a field in from the
attribute table.
- Nadir—Display the rasters with viewing angles closest to zero.
- Viewpoint—Display imagery that is closest to a selected viewing angle.
- Seamline—Smooth transitions between images using seamlines.
Default Mosaic Methods
(optional)
Choose the mosaic method that you prefer your views use. The default must be
set in the Allowed Mosaic Methods parameter list or already set in the mosaic
dataset's Allowed Mosaic Methods property.
- None—Order rasters based on the ObjectID in the mosaic dataset attribute
table.
- Center—Display imagery that is closest to the center of the screen.
- NorthWest—Display imagery that is closest to the northwest corner of the
mosaic dataset boundary.
- LockRaster—Select specific raster datasets to display.
- ByAttribute—Display and prioritize imagery based on a field in from the
attribute table.
- Nadir—Display the rasters with viewing angles closest to zero.
- Viewpoint—Display imagery that is closest to a selected viewing angle.
- Seamline—Smooth transitions between images using seamlines.
Product Definition
(optional)
Select a template that is either specific to the type of imagery you are
working with or is generic. The generic options include the standard supported
raster sensor types as follows:
- NONE—No band ordering is specified for the mosaic dataset. This is the
default.
- NATURAL_COLOR_RGB—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset, with red, green, and blue
wavelength ranges. This is designed for natural color imagery.
- NATURAL_COLOR_RGBI—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset, with red, green, blue,
and near infrared wavelength ranges.
- VECTOR_FIELD_UV—Create a mosaic dataset displaying two variables.
- VECTOR_FIELD_MAGNITUDE_DIRECTION—Create a mosaic dataset displaying
magnitude and direction.
- FALSE_COLOR_IRG—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset, with near infrared, red, and
green wavelength ranges.
- DMCII_3BANDS—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset using the DMCii wavelength
ranges.
- DEIMOS2_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Deimos-2 wavelength
ranges.
- DUBAISAT-2_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the DubaiSat-2
wavelength ranges.
- FORMOSAT-2_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the FORMOSAT-2
wavelength ranges.
- GEOEYE-1_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the GeoEye-1 wavelength
ranges.
- GF-1 PMS_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Gaofen-1
Panchromatic Multispectral Sensor wavelength ranges.
- GF-1 WFV_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Gaofen-1 Wide Field
of View Sensor wavelength ranges.
- GF-2 PMS_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Gaofen-2
Panchromatic Multispectral Sensor wavelength ranges.
- GF-4 PMI_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Gaofen-4
panchromatic and multispectral wavelength ranges.
- HJ 1A/1B CCD_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Huan Jing-1 CCD
Multispectral or Hyperspectral Sensor wavelength ranges.
- IKONOS_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the IKONOS wavelength
ranges.
- JILIN-1_3BANDS—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset using the Jilin-1 wavelength
ranges.
- KOMPSAT-2_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the KOMPSAT-2
wavelength ranges.
- KOMPSAT-3_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the KOMPSAT-3
wavelength ranges.
- LANDSAT_6BANDS—Create a 6-band mosaic dataset using the Landsat 5 and 7
wavelength ranges from the TM and ETM+ sensors.
- LANDSAT_8BANDS—Create an 8-band mosaic dataset using the LANDSAT 8
wavelength ranges.
- LANDSAT_MSS_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Landsat
wavelength ranges from the MSS sensor.
- PLEIADES-1_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the PLEIADES-1
wavelength ranges.
- QUICKBIRD_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the QuickBird
wavelength ranges.
- RAPIDEYE_5BANDS—Create a 5-band mosaic dataset using the RapidEye wavelength
ranges.
- SENTINEL2_13BANDS—Create a 13-band mosaic dataset using the Sentinel 2 MSI
wavelength ranges.
- SKYSAT_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the SkySat-C MSI
wavelength ranges.
- SPOT-5_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the SPOT-5 wavelength
ranges.
- SPOT-6_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the SPOT-6 wavelength
ranges.
- SPOT-7_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the SPOT-7 wavelength
ranges.
- TH-01_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Tian Hui-1 wavelength
ranges.
- WORLDVIEW-2_8BANDS—Create an 8-band mosaic dataset using the WorldView-2
wavelength ranges.
- WORLDVIEW-3_8BANDS—Create an 8-band mosaic dataset using the WorldView-3
wavelength ranges.
- WORLDVIEW-4_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the WorldView-4
wavelength ranges.
- ZY1-02C PMS_3BANDS—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset using the ZiYuan-1
panchromatic/multispectral wavelength ranges.
- ZY3-CRESDA_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the ZiYuan-3 CRESDA
wavelength ranges.
- ZY3-SASMAC_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the ZiYuan-3 SASMAC
wavelength ranges.
- CUSTOM—Define the number of bands and the average wavelength for each band.
Product Band Definitions
(optional)
Edit Product Definition by adjusting the wavelength ranges, changing the
number of bands or the band order, and adding new bands.
Order Field
(optional)
Choose the default field to use when ordering rasters using the By Attribute
mosaic method.
The list of fields is defined as those in the attribute table
that are of type metadata and are integer. This list can include, but is not
limited to:
- Name
- MinPS
- MaxPS
- LowPS
- HighPS
- Tag
- GroupName
- ProductName
- CenterX
- CenterY
- ZOrder
- Shape_Length
- Shape_Area
If your field is a numeric or date field, then the Order Base parameter needs
to be set.
This parameter is not needed if By Attribute is not an allowed mosaic
method.
Order Base
(optional)
Sort the rasters based on their difference from this value in the field
selected in the Order Field parameter.
If you are using a Date attribute, then it needs to be in one of the
following formats:
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm:ss.s
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm:ss
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm
- YYYY/MM/DD HH
- YYYY/MM/DD
- YYYY/MM
- YYYY
Sorting Order Ascending
(optional)
Sort ascending or descending.
- Checked—Sort ascending. This is the default setting.
- Unchecked—Sort descending.
Mosaic Operator
(optional)
Define rules for resolving overlapping pixels.
- FIRST—Display the first image within the attribute table.
- LAST—Display the last image within the attribute table.
- MIN—Display the lowest pixel values.
- MAX—Display the highest pixel values.
- MEAN—Use arithmetic mean to average overlapping pixels.
- BLEND—Use a distance weighted algorithm to average overlapping pixels.
- SUM—Add all of the overlapping pixel values.
Blend Width
(optional)
The number of pixels over which to apply the Blend Mosaic Operator.
View Point Spacing X
(optional)
When using the viewpoint mosaic method, you can horizontally shift the center
of the image using this parameter. The units are the same as the spatial
reference system.
View Point Spacing Y
(optional)
When using the viewpoint mosaic method, you can vertically shift the center
of the image using this parameter. The units are the same as the spatial
reference system.
Max
Number Per Mosaic (optional)
Set the maximum number of raster datasets that can be displayed at a given
time in a mosaic dataset.
Cell Size Tolerance
Factor (optional)
Consider images of similar spatial resolutions as having the same nominal
resolution. For example, with a factor of 0.1, all images with cell sizes within
10 percent of each other will be grouped together for tools and operations that
use cell sizes.
Output Cell Size
(optional)
Set the cell size of the mosaic dataset using an existing raster dataset or
specify its width (x) and height (y).
Metadata Level
(optional)
Set the level of metadata to expose from the server to a client when
publishing the mosaic dataset.
- FULL—Transmit metadata about processing applied at the mosaic dataset level
as well as metadata related to the individual raster datasets.
- NONE—No metadata will be exposed to the client.
- BASIC—Transmit metadata related to individual raster datasets, such as the
number of columns and rows, cell size, and spatial reference information.
Allowed Transmission
Field (optional)
Limit the fields in the attribute table that clients can view. By default,
the list includes:
- Name
- MinPS
- MaxPS
- LowPS
- HighPS
- Tag
- GroupName
- ProductName
- CenterX
- CenterY
- ZOrder
- Shape_Length
- Shape_Area
Use
Time (optional)
Enable animation through time on the mosaic dataset. If time is activated,
you need to specify the start and end fields, and the time format.
- Unchecked—The mosaic dataset will not be time aware. This is the default.
- Checked—The mosaic dataset will be time aware. This allows the client to use
the Time Slider.
Start Time Field
(optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the start time.
End
Time Field (optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the end time.
Time Format
(optional)
Select the format that represents time in the fields chosen above.
- YYYY—Year
- YYYYMM—Year and month
- YYYY/MM—Year and month
- YYYY-MM—Year and month
- YYYYMMDD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY/MM/DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY-MM-DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction of
seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
Geographic
Transformation (optional)
The geographic transformations to associate with this mosaic
dataset.
Max
Number of Download Items (optional)
Limit the number of raster datasets that can be downloaded per
request.
Max
Number of Records Returned (optional)
Limit the number of records that can be downloaded per request.
Minimum Pixel
Contribution (optional)
Set the minimum number of pixels required for a mosaic dataset item to be
considered significant enough to be used in the mosaic dataset. Because of
overlapping imagery, you may have an item that is displaying a small sliver of
its overall image. Skipping these mosaic dataset items will help the performance
of the mosaic dataset.
Time Interval
(optional)
Specify the duration that represents each time step interval. The time step
interval defines the granularity of the temporal data. The unit of time is
specified in the Time Interval Units parameter.
Time Interval Units
(optional)
Choose the appropriate units for your time interval.
- None—There is no time unit, or the units are unknown.
- Milliseconds—The time units are in milliseconds.
- Seconds—The time units are in seconds.
- Minutes—The time units are in minutes.
- Hours—The time units are in hours.
- Days—The time units are in days.
- Weeks—The time units are in weeks.
- Months—The time units are in months.
- Years—The time units are in years.
- Decades—The time units are in decades.
17. Default Processing Template (optional)
Define the default function chain. The default function chain will be applied when the mosaic dataset is accessed.
18. Allowed Mosaic Methods (optional)
Define the rules for displaying overlapping imagery.
- None—Order rasters based on the ObjectID in the mosaic dataset attribute
table.
- Center—Display imagery that is closest to the center of the screen.
- NorthWest—Display imagery that is closest to the northwest corner of the
mosaic dataset boundary.
- LockRaster—Select specific raster datasets to display.
- ByAttribute—Display and prioritize imagery based on a field in from the
attribute table.
- Nadir—Display the rasters with viewing angles closest to zero.
- Viewpoint—Display imagery that is closest to a selected viewing angle.
- Seamline—Smooth transitions between images using seamlines.
Default Mosaic Methods
(optional)
Choose the mosaic method that you prefer your views use. The default must be
set in the Allowed Mosaic Methods parameter list or already set in the mosaic
dataset's Allowed Mosaic Methods property.
- None—Order rasters based on the ObjectID in the mosaic dataset attribute
table.
- Center—Display imagery that is closest to the center of the screen.
- NorthWest—Display imagery that is closest to the northwest corner of the
mosaic dataset boundary.
- LockRaster—Select specific raster datasets to display.
- ByAttribute—Display and prioritize imagery based on a field in from the
attribute table.
- Nadir—Display the rasters with viewing angles closest to zero.
- Viewpoint—Display imagery that is closest to a selected viewing angle.
- Seamline—Smooth transitions between images using seamlines.
Product Definition
(optional)
Select a template that is either specific to the type of imagery you are
working with or is generic. The generic options include the standard supported
raster sensor types as follows:
- NONE—No band ordering is specified for the mosaic dataset. This is the
default.
- NATURAL_COLOR_RGB—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset, with red, green, and blue
wavelength ranges. This is designed for natural color imagery.
- NATURAL_COLOR_RGBI—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset, with red, green, blue,
and near infrared wavelength ranges.
- VECTOR_FIELD_UV—Create a mosaic dataset displaying two variables.
- VECTOR_FIELD_MAGNITUDE_DIRECTION—Create a mosaic dataset displaying
magnitude and direction.
- FALSE_COLOR_IRG—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset, with near infrared, red, and
green wavelength ranges.
- DMCII_3BANDS—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset using the DMCii wavelength
ranges.
- DEIMOS2_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Deimos-2 wavelength
ranges.
- DUBAISAT-2_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the DubaiSat-2
wavelength ranges.
- FORMOSAT-2_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the FORMOSAT-2
wavelength ranges.
- GEOEYE-1_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the GeoEye-1 wavelength
ranges.
- GF-1 PMS_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Gaofen-1
Panchromatic Multispectral Sensor wavelength ranges.
- GF-1 WFV_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Gaofen-1 Wide Field
of View Sensor wavelength ranges.
- GF-2 PMS_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Gaofen-2
Panchromatic Multispectral Sensor wavelength ranges.
- GF-4 PMI_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Gaofen-4
panchromatic and multispectral wavelength ranges.
- HJ 1A/1B CCD_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Huan Jing-1 CCD
Multispectral or Hyperspectral Sensor wavelength ranges.
- IKONOS_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the IKONOS wavelength
ranges.
- JILIN-1_3BANDS—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset using the Jilin-1 wavelength
ranges.
- KOMPSAT-2_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the KOMPSAT-2
wavelength ranges.
- KOMPSAT-3_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the KOMPSAT-3
wavelength ranges.
- LANDSAT_6BANDS—Create a 6-band mosaic dataset using the Landsat 5 and 7
wavelength ranges from the TM and ETM+ sensors.
- LANDSAT_8BANDS—Create an 8-band mosaic dataset using the LANDSAT 8
wavelength ranges.
- LANDSAT_MSS_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Landsat
wavelength ranges from the MSS sensor.
- PLEIADES-1_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the PLEIADES-1
wavelength ranges.
- QUICKBIRD_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the QuickBird
wavelength ranges.
- RAPIDEYE_5BANDS—Create a 5-band mosaic dataset using the RapidEye wavelength
ranges.
- SENTINEL2_13BANDS—Create a 13-band mosaic dataset using the Sentinel 2 MSI
wavelength ranges.
- SKYSAT_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the SkySat-C MSI
wavelength ranges.
- SPOT-5_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the SPOT-5 wavelength
ranges.
- SPOT-6_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the SPOT-6 wavelength
ranges.
- SPOT-7_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the SPOT-7 wavelength
ranges.
- TH-01_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Tian Hui-1 wavelength
ranges.
- WORLDVIEW-2_8BANDS—Create an 8-band mosaic dataset using the WorldView-2
wavelength ranges.
- WORLDVIEW-3_8BANDS—Create an 8-band mosaic dataset using the WorldView-3
wavelength ranges.
- WORLDVIEW-4_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the WorldView-4
wavelength ranges.
- ZY1-02C PMS_3BANDS—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset using the ZiYuan-1
panchromatic/multispectral wavelength ranges.
- ZY3-CRESDA_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the ZiYuan-3 CRESDA
wavelength ranges.
- ZY3-SASMAC_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the ZiYuan-3 SASMAC
wavelength ranges.
- CUSTOM—Define the number of bands and the average wavelength for each band.
Product Band Definitions
(optional)
Edit Product Definition by adjusting the wavelength ranges, changing the
number of bands or the band order, and adding new bands.
Order Field
(optional)
Choose the default field to use when ordering rasters using the By Attribute
mosaic method. The list of fields is defined as those in the attribute table
that are of type metadata and are integer. This list can include, but is not
limited to:
- Name
- MinPS
- MaxPS
- LowPS
- HighPS
- Tag
- GroupName
- ProductName
- CenterX
- CenterY
- ZOrder
- Shape_Length
- Shape_Area
If your field is a numeric or date field, then the Order Base parameter needs
to be set.
This parameter is not needed if By Attribute is not an allowed mosaic
method.
Order Base
(optional)
Sort the rasters based on their difference from this value in the field
selected in the Order Field parameter.
If you are using a Date attribute, then it needs to be in one of the
following formats:
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm:ss.s
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm:ss
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm
- YYYY/MM/DD HH
- YYYY/MM/DD
- YYYY/MM
- YYYY
Sorting Order Ascending
(optional)
Sort ascending or descending.
- Checked—Sort ascending. This is the default setting.
- Unchecked—Sort descending.
Mosaic Operator
(optional)
Define rules for resolving overlapping pixels.
- FIRST—Display the first image within the attribute table.
- LAST—Display the last image within the attribute table.
- MIN—Display the lowest pixel values.
- MAX—Display the highest pixel values.
- MEAN—Use arithmetic mean to average overlapping pixels.
- BLEND—Use a distance weighted algorithm to average overlapping pixels.
- SUM—Add all of the overlapping pixel values.
Blend Width
(optional)
The number of pixels over which to apply the Blend Mosaic Operator.
View Point Spacing X
(optional)
When using the viewpoint mosaic method, you can horizontally shift the center
of the image using this parameter. The units are the same as the spatial
reference system.
View Point Spacing Y
(optional)
When using the viewpoint mosaic method, you can vertically shift the center
of the image using this parameter. The units are the same as the spatial
reference system.
Max
Number Per Mosaic (optional)
Set the maximum number of raster datasets that can be displayed at a given
time in a mosaic dataset.
Cell Size Tolerance
Factor (optional)
Consider images of similar spatial resolutions as having the same nominal
resolution. For example, with a factor of 0.1, all images with cell sizes within
10 percent of each other will be grouped together for tools and operations that
use cell sizes.
Output Cell Size
(optional)
Set the cell size of the mosaic dataset using an existing raster dataset or
specify its width (x) and height (y).
Metadata Level
(optional)
Set the level of metadata to expose from the server to a client when
publishing the mosaic dataset.
- FULL—Transmit metadata about processing applied at the mosaic dataset level
as well as metadata related to the individual raster datasets.
- NONE—No metadata will be exposed to the client.
- BASIC—Transmit metadata related to individual raster datasets, such as the
number of columns and rows, cell size, and spatial reference information.
Allowed Transmission
Field (optional)
Limit the fields in the attribute table that clients can view. By default,
the list includes:
- Name
- MinPS
- MaxPS
- LowPS
- HighPS
- Tag
- GroupName
- ProductName
- CenterX
- CenterY
- ZOrder
- Shape_Length
- Shape_Area
Use
Time (optional)
Enable animation through time on the mosaic dataset. If time is activated,
you need to specify the start and end fields, and the time format.
- Unchecked—The mosaic dataset will not be time aware. This is the default.
- Checked—The mosaic dataset will be time aware. This allows the client to use
the Time Slider.
Start Time Field
(optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the start time.
End
Time Field (optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the end time.
Time Format
(optional)
Select the format that represents time in the fields chosen above.
- YYYY—Year
- YYYYMM—Year and month
- YYYY/MM—Year and month
- YYYY-MM—Year and month
- YYYYMMDD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY/MM/DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY-MM-DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction of
seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
Geographic
Transformation (optional)
The geographic transformations to associate with this mosaic
dataset.
Max
Number of Download Items (optional)
Limit the number of raster datasets that can be downloaded per
request.
Max
Number of Records Returned (optional)
Limit the number of records that can be downloaded per request.
Minimum Pixel
Contribution (optional)
Set the minimum number of pixels required for a mosaic dataset item to be
considered significant enough to be used in the mosaic dataset. Because of
overlapping imagery, you may have an item that is displaying a small sliver of
its overall image. Skipping these mosaic dataset items will help the performance
of the mosaic dataset.
Time Interval
(optional)
Specify the duration that represents each time step interval. The time step
interval defines the granularity of the temporal data. The unit of time is
specified in the Time Interval Units parameter.
Time Interval Units
(optional)
Choose the appropriate units for your time interval.
- None—There is no time unit, or the units are unknown.
- Milliseconds—The time units are in milliseconds.
- Seconds—The time units are in seconds.
- Minutes—The time units are in minutes.
- Hours—The time units are in hours.
- Days—The time units are in days.
- Weeks—The time units are in weeks.
- Months—The time units are in months.
- Years—The time units are in years.
- Decades—The time units are in decades.
19. Default Mosaic Methods (optional)
Choose the mosaic method that you prefer your views use. The default must be
set in the Allowed Mosaic Methods parameter list or already set in the mosaic
dataset's Allowed Mosaic Methods property.
- None—Order rasters based on the ObjectID in the mosaic dataset attribute
table.
- Center—Display imagery that is closest to the center of the screen.
- NorthWest—Display imagery that is closest to the northwest corner of the
mosaic dataset boundary.
- LockRaster—Select specific raster datasets to display.
- ByAttribute—Display and prioritize imagery based on a field in from the
attribute table.
- Nadir—Display the rasters with viewing angles closest to zero.
- Viewpoint—Display imagery that is closest to a selected viewing angle.
- Seamline—Smooth transitions between images using seamlines.
Product Definition
(optional)
Select a template that is either specific to the type of imagery you are
working with or is generic. The generic options include the standard supported
raster sensor types as follows:
- NONE—No band ordering is specified for the mosaic dataset. This is the
default.
- NATURAL_COLOR_RGB—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset, with red, green, and blue
wavelength ranges. This is designed for natural color imagery.
- NATURAL_COLOR_RGBI—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset, with red, green, blue,
and near infrared wavelength ranges.
- VECTOR_FIELD_UV—Create a mosaic dataset displaying two variables.
- VECTOR_FIELD_MAGNITUDE_DIRECTION—Create a mosaic dataset displaying
magnitude and direction.
- FALSE_COLOR_IRG—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset, with near infrared, red, and
green wavelength ranges.
- DMCII_3BANDS—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset using the DMCii wavelength
ranges.
- DEIMOS2_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Deimos-2 wavelength
ranges.
- DUBAISAT-2_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the DubaiSat-2
wavelength ranges.
- FORMOSAT-2_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the FORMOSAT-2
wavelength ranges.
- GEOEYE-1_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the GeoEye-1 wavelength
ranges.
- GF-1 PMS_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Gaofen-1
Panchromatic Multispectral Sensor wavelength ranges.
- GF-1 WFV_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Gaofen-1 Wide Field
of View Sensor wavelength ranges.
- GF-2 PMS_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Gaofen-2
Panchromatic Multispectral Sensor wavelength ranges.
- GF-4 PMI_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Gaofen-4
panchromatic and multispectral wavelength ranges.
- HJ 1A/1B CCD_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Huan Jing-1 CCD
Multispectral or Hyperspectral Sensor wavelength ranges.
- IKONOS_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the IKONOS wavelength
ranges.
- JILIN-1_3BANDS—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset using the Jilin-1 wavelength
ranges.
- KOMPSAT-2_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the KOMPSAT-2
wavelength ranges.
- KOMPSAT-3_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the KOMPSAT-3
wavelength ranges.
- LANDSAT_6BANDS—Create a 6-band mosaic dataset using the Landsat 5 and 7
wavelength ranges from the TM and ETM+ sensors.
- LANDSAT_8BANDS—Create an 8-band mosaic dataset using the LANDSAT 8
wavelength ranges.
- LANDSAT_MSS_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Landsat
wavelength ranges from the MSS sensor.
- PLEIADES-1_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the PLEIADES-1
wavelength ranges.
- QUICKBIRD_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the QuickBird
wavelength ranges.
- RAPIDEYE_5BANDS—Create a 5-band mosaic dataset using the RapidEye wavelength
ranges.
- SENTINEL2_13BANDS—Create a 13-band mosaic dataset using the Sentinel 2 MSI
wavelength ranges.
- SKYSAT_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the SkySat-C MSI
wavelength ranges.
- SPOT-5_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the SPOT-5 wavelength
ranges.
- SPOT-6_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the SPOT-6 wavelength
ranges.
- SPOT-7_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the SPOT-7 wavelength
ranges.
- TH-01_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Tian Hui-1 wavelength
ranges.
- WORLDVIEW-2_8BANDS—Create an 8-band mosaic dataset using the WorldView-2
wavelength ranges.
- WORLDVIEW-3_8BANDS—Create an 8-band mosaic dataset using the WorldView-3
wavelength ranges.
- WORLDVIEW-4_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the WorldView-4
wavelength ranges.
- ZY1-02C PMS_3BANDS—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset using the ZiYuan-1
panchromatic/multispectral wavelength ranges.
- ZY3-CRESDA_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the ZiYuan-3 CRESDA
wavelength ranges.
- ZY3-SASMAC_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the ZiYuan-3 SASMAC
wavelength ranges.
- CUSTOM—Define the number of bands and the average wavelength for each band.
Product Band Definitions
(optional)
Edit Product Definition by adjusting the wavelength ranges, changing the
number of bands or the band order, and adding new bands.
Order Field
(optional)
Choose the default field to use when ordering rasters using the By Attribute
mosaic method. The list of fields is defined as those in the attribute table
that are of type metadata and are integer. This list can include, but is not
limited to:
- Name
- MinPS
- MaxPS
- LowPS
- HighPS
- Tag
- GroupName
- ProductName
- CenterX
- CenterY
- ZOrder
- Shape_Length
- Shape_Area
If your field is a numeric or date field, then the Order Base parameter needs
to be set.
This parameter is not needed if By Attribute is not an allowed mosaic
method.
Order Base
(optional)
Sort the rasters based on their difference from this value in the field
selected in the Order Field parameter.
If you are using a Date attribute, then it needs to be in one of the
following formats:
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm:ss.s
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm:ss
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm
- YYYY/MM/DD HH
- YYYY/MM/DD
- YYYY/MM
- YYYY
Sorting Order Ascending
(optional)
Sort ascending or descending.
- Checked—Sort ascending. This is the default setting.
- Unchecked—Sort descending.
Mosaic Operator
(optional)
Define rules for resolving overlapping pixels.
- FIRST—Display the first image within the attribute table.
- LAST—Display the last image within the attribute table.
- MIN—Display the lowest pixel values.
- MAX—Display the highest pixel values.
- MEAN—Use arithmetic mean to average overlapping pixels.
- BLEND—Use a distance weighted algorithm to average overlapping pixels.
- SUM—Add all of the overlapping pixel values.
Blend Width
(optional)
The number of pixels over which to apply the Blend Mosaic Operator.
View Point Spacing X
(optional)
When using the viewpoint mosaic method, you can horizontally shift the center
of the image using this parameter. The units are the same as the spatial
reference system.
View Point Spacing Y
(optional)
When using the viewpoint mosaic method, you can vertically shift the center
of the image using this parameter. The units are the same as the spatial
reference system.
Max
Number Per Mosaic (optional)
Set the maximum number of raster datasets that can be displayed at a given
time in a mosaic dataset.
Cell Size Tolerance
Factor (optional)
Consider images of similar spatial resolutions as having the same nominal
resolution. For example, with a factor of 0.1, all images with cell sizes within
10 percent of each other will be grouped together for tools and operations that
use cell sizes.
Output Cell Size
(optional)
Set the cell size of the mosaic dataset using an existing raster dataset or
specify its width (x) and height (y).
Metadata Level
(optional)
Set the level of metadata to expose from the server to a client when
publishing the mosaic dataset.
- FULL—Transmit metadata about processing applied at the mosaic dataset level
as well as metadata related to the individual raster datasets.
- NONE—No metadata will be exposed to the client.
- BASIC—Transmit metadata related to individual raster datasets, such as the
number of columns and rows, cell size, and spatial reference information.
Allowed Transmission
Field (optional)
Limit the fields in the attribute table that clients can view. By default,
the list includes:
- Name
- MinPS
- MaxPS
- LowPS
- HighPS
- Tag
- GroupName
- ProductName
- CenterX
- CenterY
- ZOrder
- Shape_Length
- Shape_Area
Use
Time (optional)
Enable animation through time on the mosaic dataset. If time is activated,
you need to specify the start and end fields, and the time format.
- Unchecked—The mosaic dataset will not be time aware. This is the default.
- Checked—The mosaic dataset will be time aware. This allows the client to use
the Time Slider.
Start Time Field
(optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the start time.
End
Time Field (optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the end time.
Time Format
(optional)
Select the format that represents time in the fields chosen above.
- YYYY—Year
- YYYYMM—Year and month
- YYYY/MM—Year and month
- YYYY-MM—Year and month
- YYYYMMDD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY/MM/DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY-MM-DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction of
seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
Geographic
Transformation (optional)
The geographic transformations to associate with this mosaic
dataset.
Max
Number of Download Items (optional)
Limit the number of raster datasets that can be downloaded per
request.
Max
Number of Records Returned (optional)
Limit the number of records that can be downloaded per request.
Minimum Pixel
Contribution (optional)
Set the minimum number of pixels required for a mosaic dataset item to be
considered significant enough to be used in the mosaic dataset. Because of
overlapping imagery, you may have an item that is displaying a small sliver of
its overall image. Skipping these mosaic dataset items will help the performance
of the mosaic dataset.
Time Interval
(optional)
Specify the duration that represents each time step interval. The time step
interval defines the granularity of the temporal data. The unit of time is
specified in the Time Interval Units parameter.
Time Interval Units
(optional)
Choose the appropriate units for your time interval.
- None—There is no time unit, or the units are unknown.
- Milliseconds—The time units are in milliseconds.
- Seconds—The time units are in seconds.
- Minutes—The time units are in minutes.
- Hours—The time units are in hours.
- Days—The time units are in days.
- Weeks—The time units are in weeks.
- Months—The time units are in months.
- Years—The time units are in years.
- Decades—The time units are in decades.
20. Product Definition (optional)
Select a template that is either specific to the type of imagery you are
working with or is generic. The generic options include the standard supported
raster sensor types as follows:
- NONE—No band ordering is specified for the mosaic dataset. This is the
default.
- NATURAL_COLOR_RGB—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset, with red, green, and blue
wavelength ranges. This is designed for natural color imagery.
- NATURAL_COLOR_RGBI—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset, with red, green, blue,
and near infrared wavelength ranges.
- VECTOR_FIELD_UV—Create a mosaic dataset displaying two variables.
- VECTOR_FIELD_MAGNITUDE_DIRECTION—Create a mosaic dataset displaying
magnitude and direction.
- FALSE_COLOR_IRG—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset, with near infrared, red, and
green wavelength ranges.
- DMCII_3BANDS—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset using the DMCii wavelength
ranges.
- DEIMOS2_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Deimos-2 wavelength
ranges.
- DUBAISAT-2_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the DubaiSat-2
wavelength ranges.
- FORMOSAT-2_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the FORMOSAT-2
wavelength ranges.
- GEOEYE-1_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the GeoEye-1 wavelength
ranges.
- GF-1 PMS_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Gaofen-1
Panchromatic Multispectral Sensor wavelength ranges.
- GF-1 WFV_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Gaofen-1 Wide Field
of View Sensor wavelength ranges.
- GF-2 PMS_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Gaofen-2
Panchromatic Multispectral Sensor wavelength ranges.
- GF-4 PMI_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Gaofen-4
panchromatic and multispectral wavelength ranges.
- HJ 1A/1B CCD_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Huan Jing-1 CCD
Multispectral or Hyperspectral Sensor wavelength ranges.
- IKONOS_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the IKONOS wavelength
ranges.
- JILIN-1_3BANDS—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset using the Jilin-1 wavelength
ranges.
- KOMPSAT-2_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the KOMPSAT-2
wavelength ranges.
- KOMPSAT-3_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the KOMPSAT-3
wavelength ranges.
- LANDSAT_6BANDS—Create a 6-band mosaic dataset using the Landsat 5 and 7
wavelength ranges from the TM and ETM+ sensors.
- LANDSAT_8BANDS—Create an 8-band mosaic dataset using the LANDSAT 8
wavelength ranges.
- LANDSAT_MSS_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Landsat
wavelength ranges from the MSS sensor.
- PLEIADES-1_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the PLEIADES-1
wavelength ranges.
- QUICKBIRD_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the QuickBird
wavelength ranges.
- RAPIDEYE_5BANDS—Create a 5-band mosaic dataset using the RapidEye wavelength
ranges.
- SENTINEL2_13BANDS—Create a 13-band mosaic dataset using the Sentinel 2 MSI
wavelength ranges.
- SKYSAT_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the SkySat-C MSI
wavelength ranges.
- SPOT-5_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the SPOT-5 wavelength
ranges.
- SPOT-6_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the SPOT-6 wavelength
ranges.
- SPOT-7_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the SPOT-7 wavelength
ranges.
- TH-01_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the Tian Hui-1 wavelength
ranges.
- WORLDVIEW-2_8BANDS—Create an 8-band mosaic dataset using the WorldView-2
wavelength ranges.
- WORLDVIEW-3_8BANDS—Create an 8-band mosaic dataset using the WorldView-3
wavelength ranges.
- WORLDVIEW-4_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the WorldView-4
wavelength ranges.
- ZY1-02C PMS_3BANDS—Create a 3-band mosaic dataset using the ZiYuan-1
panchromatic/multispectral wavelength ranges.
- ZY3-CRESDA_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the ZiYuan-3 CRESDA
wavelength ranges.
- ZY3-SASMAC_4BANDS—Create a 4-band mosaic dataset using the ZiYuan-3 SASMAC
wavelength ranges.
- CUSTOM—Define the number of bands and the average wavelength for each band.
Product Band Definitions
(optional)
Edit Product Definition by adjusting the wavelength ranges, changing the
number of bands or the band order, and adding new bands.
Order Field
(optional)
Choose the default field to use when ordering rasters using the By Attribute
mosaic method. The list of fields is defined as those in the attribute table
that are of type metadata and are integer. This list can include, but is not
limited to:
- Name
- MinPS
- MaxPS
- LowPS
- HighPS
- Tag
- GroupName
- ProductName
- CenterX
- CenterY
- ZOrder
- Shape_Length
- Shape_Area
If your field is a numeric or date field, then the Order Base parameter needs
to be set.
This parameter is not needed if By Attribute is not an allowed mosaic
method.
Order Base
(optional)
Sort the rasters based on their difference from this value in the field
selected in the Order Field parameter.
If you are using a Date attribute, then it needs to be in one of the
following formats:
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm:ss.s
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm:ss
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm
- YYYY/MM/DD HH
- YYYY/MM/DD
- YYYY/MM
- YYYY
Sorting Order Ascending
(optional)
Sort ascending or descending.
- Checked—Sort ascending. This is the default setting.
- Unchecked—Sort descending.
Mosaic Operator
(optional)
Define rules for resolving overlapping pixels.
- FIRST—Display the first image within the attribute table.
- LAST—Display the last image within the attribute table.
- MIN—Display the lowest pixel values.
- MAX—Display the highest pixel values.
- MEAN—Use arithmetic mean to average overlapping pixels.
- BLEND—Use a distance weighted algorithm to average overlapping pixels.
- SUM—Add all of the overlapping pixel values.
Blend Width
(optional)
The number of pixels over which to apply the Blend Mosaic Operator.
View Point Spacing X
(optional)
When using the viewpoint mosaic method, you can horizontally shift the center
of the image using this parameter. The units are the same as the spatial
reference system.
View Point Spacing Y
(optional)
When using the viewpoint mosaic method, you can vertically shift the center
of the image using this parameter. The units are the same as the spatial
reference system.
Max
Number Per Mosaic (optional)
Set the maximum number of raster datasets that can be displayed at a given
time in a mosaic dataset.
Cell Size Tolerance
Factor (optional)
Consider images of similar spatial resolutions as having the same nominal
resolution. For example, with a factor of 0.1, all images with cell sizes within
10 percent of each other will be grouped together for tools and operations that
use cell sizes.
Output Cell Size
(optional)
Set the cell size of the mosaic dataset using an existing raster dataset or
specify its width (x) and height (y).
Metadata Level
(optional)
Set the level of metadata to expose from the server to a client when
publishing the mosaic dataset.
- FULL—Transmit metadata about processing applied at the mosaic dataset level
as well as metadata related to the individual raster datasets.
- NONE—No metadata will be exposed to the client.
- BASIC—Transmit metadata related to individual raster datasets, such as the
number of columns and rows, cell size, and spatial reference information.
Allowed Transmission
Field (optional)
Limit the fields in the attribute table that clients can view. By default,
the list includes:
- Name
- MinPS
- MaxPS
- LowPS
- HighPS
- Tag
- GroupName
- ProductName
- CenterX
- CenterY
- ZOrder
- Shape_Length
- Shape_Area
Use
Time (optional)
Enable animation through time on the mosaic dataset. If time is activated,
you need to specify the start and end fields, and the time format.
- Unchecked—The mosaic dataset will not be time aware. This is the default.
- Checked—The mosaic dataset will be time aware. This allows the client to use
the Time Slider.
Start Time Field
(optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the start time.
End
Time Field (optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the end time.
Time Format
(optional)
Select the format that represents time in the fields chosen above.
- YYYY—Year
- YYYYMM—Year and month
- YYYY/MM—Year and month
- YYYY-MM—Year and month
- YYYYMMDD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY/MM/DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY-MM-DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction of
seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
Geographic
Transformation (optional)
The geographic transformations to associate with this mosaic
dataset.
Max
Number of Download Items (optional)
Limit the number of raster datasets that can be downloaded per
request.
Max
Number of Records Returned (optional)
Limit the number of records that can be downloaded per request.
Minimum Pixel
Contribution (optional)
Set the minimum number of pixels required for a mosaic dataset item to be
considered significant enough to be used in the mosaic dataset. Because of
overlapping imagery, you may have an item that is displaying a small sliver of
its overall image.
Skipping these mosaic dataset items will help the performance
of the mosaic dataset.
Time Interval
(optional)
Specify the duration that represents each time step interval. The time step
interval defines the granularity of the temporal data. The unit of time is
specified in the Time Interval Units parameter.
Time Interval Units
(optional)
Choose the appropriate units for your time interval.
- None—There is no time unit, or the units are unknown.
- Milliseconds—The time units are in milliseconds.
- Seconds—The time units are in seconds.
- Minutes—The time units are in minutes.
- Hours—The time units are in hours.
- Days—The time units are in days.
- Weeks—The time units are in weeks.
- Months—The time units are in months.
- Years—The time units are in years.
- Decades—The time units are in decades.
21. Product Band Definitions (optional)
Edit Product Definition by adjusting the wavelength ranges, changing the
number of bands or the band order, and adding new bands.
Order Field
(optional)
Choose the default field to use when ordering rasters using the By Attribute
mosaic method. The list of fields is defined as those in the attribute table
that are of type metadata and are integer. This list can include, but is not
limited to:
- Name
- MinPS
- MaxPS
- LowPS
- HighPS
- Tag
- GroupName
- ProductName
- CenterX
- CenterY
- ZOrder
- Shape_Length
- Shape_Area
If your field is a numeric or date field, then the Order Base parameter needs
to be set.
This parameter is not needed if By Attribute is not an allowed mosaic
method.
Order Base
(optional)
Sort the rasters based on their difference from this value in the field
selected in the Order Field parameter.
If you are using a Date attribute, then it needs to be in one of the
following formats:
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm:ss.s
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm:ss
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm
- YYYY/MM/DD HH
- YYYY/MM/DD
- YYYY/MM
- YYYY
Sorting Order Ascending
(optional)
Sort ascending or descending.
- Checked—Sort ascending. This is the default setting.
- Unchecked—Sort descending.
Mosaic Operator
(optional)
Define rules for resolving overlapping pixels.
- FIRST—Display the first image within the attribute table.
- LAST—Display the last image within the attribute table.
- MIN—Display the lowest pixel values.
- MAX—Display the highest pixel values.
- MEAN—Use arithmetic mean to average overlapping pixels.
- BLEND—Use a distance weighted algorithm to average overlapping pixels.
- SUM—Add all of the overlapping pixel values.
Blend Width
(optional)
The number of pixels over which to apply the Blend Mosaic Operator.
View Point Spacing X
(optional)
When using the viewpoint mosaic method, you can horizontally shift the center
of the image using this parameter. The units are the same as the spatial
reference system.
View Point Spacing Y
(optional)
When using the viewpoint mosaic method, you can vertically shift the center
of the image using this parameter. The units are the same as the spatial
reference system.
Max
Number Per Mosaic (optional)
Set the maximum number of raster datasets that can be displayed at a given
time in a mosaic dataset.
Cell Size Tolerance
Factor (optional)
Consider images of similar spatial resolutions as having the same nominal
resolution. For example, with a factor of 0.1, all images with cell sizes within
10 percent of each other will be grouped together for tools and operations that
use cell sizes.
Output Cell Size
(optional)
Set the cell size of the mosaic dataset using an existing raster dataset or
specify its width (x) and height (y).
Metadata Level
(optional)
Set the level of metadata to expose from the server to a client when
publishing the mosaic dataset.
- FULL—Transmit metadata about processing applied at the mosaic dataset level
as well as metadata related to the individual raster datasets.
- NONE—No metadata will be exposed to the client.
- BASIC—Transmit metadata related to individual raster datasets, such as the
number of columns and rows, cell size, and spatial reference information.
Allowed Transmission
Field (optional)
Limit the fields in the attribute table that clients can view. By default,
the list includes:
- Name
- MinPS
- MaxPS
- LowPS
- HighPS
- Tag
- GroupName
- ProductName
- CenterX
- CenterY
- ZOrder
- Shape_Length
- Shape_Area
Use
Time (optional)
Enable animation through time on the mosaic dataset. If time is activated,
you need to specify the start and end fields, and the time format.
- Unchecked—The mosaic dataset will not be time aware. This is the default.
- Checked—The mosaic dataset will be time aware. This allows the client to use
the Time Slider.
Start Time Field
(optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the start time.
End
Time Field (optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the end time.
Time Format
(optional)
Select the format that represents time in the fields chosen above.
- YYYY—Year
- YYYYMM—Year and month
- YYYY/MM—Year and month
- YYYY-MM—Year and month
- YYYYMMDD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY/MM/DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY-MM-DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction of
seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
Geographic
Transformation (optional)
The geographic transformations to associate with this mosaic
dataset.
Max
Number of Download Items (optional)
Limit the number of raster datasets that can be downloaded per
request.
Max
Number of Records Returned (optional)
Limit the number of records that can be downloaded per request.
Minimum Pixel
Contribution (optional)
Set the minimum number of pixels required for a mosaic dataset item to be
considered significant enough to be used in the mosaic dataset. Because of
overlapping imagery, you may have an item that is displaying a small sliver of
its overall image. Skipping these mosaic dataset items will help the performance
of the mosaic dataset.
Time Interval
(optional)
Specify the duration that represents each time step interval. The time step
interval defines the granularity of the temporal data. The unit of time is
specified in the Time Interval Units parameter.
Time Interval Units
(optional)
Choose the appropriate units for your time interval.
- None—There is no time unit, or the units are unknown.
- Milliseconds—The time units are in milliseconds.
- Seconds—The time units are in seconds.
- Minutes—The time units are in minutes.
- Hours—The time units are in hours.
- Days—The time units are in days.
- Weeks—The time units are in weeks.
- Months—The time units are in months.
- Years—The time units are in years.
- Decades—The time units are in decades.
22. Order Field (optional)
Choose the default field to use when ordering rasters using the By Attribute
mosaic method. The list of fields is defined as those in the attribute table
that are of type metadata and are integer. This list can include, but is not
limited to:
- Name
- MinPS
- MaxPS
- LowPS
- HighPS
- Tag
- GroupName
- ProductName
- CenterX
- CenterY
- ZOrder
- Shape_Length
- Shape_Area
If your field is a numeric or date field, then the Order Base parameter needs
to be set.
This parameter is not needed if By Attribute is not an allowed mosaic
method.
Order Base
(optional)
Sort the rasters based on their difference from this value in the field
selected in the Order Field parameter.
If you are using a Date attribute, then it needs to be in one of the
following formats:
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm:ss.s
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm:ss
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm
- YYYY/MM/DD HH
- YYYY/MM/DD
- YYYY/MM
- YYYY
Sorting Order Ascending
(optional)
Sort ascending or descending.
- Checked—Sort ascending. This is the default setting.
- Unchecked—Sort descending.
Mosaic Operator
(optional)
Define rules for resolving overlapping pixels.
- FIRST—Display the first image within the attribute table.
- LAST—Display the last image within the attribute table.
- MIN—Display the lowest pixel values.
- MAX—Display the highest pixel values.
- MEAN—Use arithmetic mean to average overlapping pixels.
- BLEND—Use a distance weighted algorithm to average overlapping pixels.
- SUM—Add all of the overlapping pixel values.
Blend Width
(optional)
The number of pixels over which to apply the Blend Mosaic Operator.
View Point Spacing X
(optional)
When using the viewpoint mosaic method, you can horizontally shift the center
of the image using this parameter. The units are the same as the spatial
reference system.
View Point Spacing Y
(optional)
When using the viewpoint mosaic method, you can vertically shift the center
of the image using this parameter. The units are the same as the spatial
reference system.
Max
Number Per Mosaic (optional)
Set the maximum number of raster datasets that can be displayed at a given
time in a mosaic dataset.
Cell Size Tolerance
Factor (optional)
Consider images of similar spatial resolutions as having the same nominal
resolution. For example, with a factor of 0.1, all images with cell sizes within
10 percent of each other will be grouped together for tools and operations that
use cell sizes.
Output Cell Size
(optional)
Set the cell size of the mosaic dataset using an existing raster dataset or
specify its width (x) and height (y).
Metadata Level
(optional)
Set the level of metadata to expose from the server to a client when
publishing the mosaic dataset.
- FULL—Transmit metadata about processing applied at the mosaic dataset level
as well as metadata related to the individual raster datasets.
- NONE—No metadata will be exposed to the client.
- BASIC—Transmit metadata related to individual raster datasets, such as the
number of columns and rows, cell size, and spatial reference information.
Allowed Transmission
Field (optional)
Limit the fields in the attribute table that clients can view. By default,
the list includes:
- Name
- MinPS
- MaxPS
- LowPS
- HighPS
- Tag
- GroupName
- ProductName
- CenterX
- CenterY
- ZOrder
- Shape_Length
- Shape_Area
Use
Time (optional)
Enable animation through time on the mosaic dataset. If time is activated,
you need to specify the start and end fields, and the time format.
- Unchecked—The mosaic dataset will not be time aware. This is the default.
- Checked—The mosaic dataset will be time aware. This allows the client to use
the Time Slider.
Start Time Field
(optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the start time.
End
Time Field (optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the end time.
Time Format
(optional)
Select the format that represents time in the fields chosen above.
- YYYY—Year
- YYYYMM—Year and month
- YYYY/MM—Year and month
- YYYY-MM—Year and month
- YYYYMMDD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY/MM/DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY-MM-DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction of
seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
Geographic
Transformation (optional)
The geographic transformations to associate with this mosaic
dataset.
Max
Number of Download Items (optional)
Limit the number of raster datasets that can be downloaded per
request.
Max
Number of Records Returned (optional)
Limit the number of records that can be downloaded per request.
Minimum Pixel
Contribution (optional)
Set the minimum number of pixels required for a mosaic dataset item to be
considered significant enough to be used in the mosaic dataset. Because of
overlapping imagery, you may have an item that is displaying a small sliver of
its overall image. Skipping these mosaic dataset items will help the performance
of the mosaic dataset.
Time Interval
(optional)
Specify the duration that represents each time step interval. The time step
interval defines the granularity of the temporal data. The unit of time is
specified in the Time Interval Units parameter.
Time Interval Units
(optional)
Choose the appropriate units for your time interval.
- None—There is no time unit, or the units are unknown.
- Milliseconds—The time units are in milliseconds.
- Seconds—The time units are in seconds.
- Minutes—The time units are in minutes.
- Hours—The time units are in hours.
- Days—The time units are in days.
- Weeks—The time units are in weeks.
- Months—The time units are in months.
- Years—The time units are in years.
- Decades—The time units are in decades.
23. Order Base (optional)
Sort the rasters based on their difference from this value in the field
selected in the Order Field parameter.
If you are using a Date attribute, then it needs to be in one of the
following formats:
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm:ss.s
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm:ss
- YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm
- YYYY/MM/DD HH
- YYYY/MM/DD
- YYYY/MM
- YYYY
24. Sorting Order Ascending (optional)
Sort ascending or descending.
- Checked—Sort ascending. This is the default setting.
- Unchecked—Sort descending.
Mosaic Operator
(optional)
Define rules for resolving overlapping pixels.
- FIRST—Display the first image within the attribute table.
- LAST—Display the last image within the attribute table.
- MIN—Display the lowest pixel values.
- MAX—Display the highest pixel values.
- MEAN—Use arithmetic mean to average overlapping pixels.
- BLEND—Use a distance weighted algorithm to average overlapping pixels.
- SUM—Add all of the overlapping pixel values.
Blend Width
(optional)
The number of pixels over which to apply the Blend Mosaic Operator.
View Point Spacing X
(optional)
When using the viewpoint mosaic method, you can horizontally shift the center
of the image using this parameter. The units are the same as the spatial
reference system.
View Point Spacing Y
(optional)
When using the viewpoint mosaic method, you can vertically shift the center
of the image using this parameter. The units are the same as the spatial
reference system.
Max
Number Per Mosaic (optional)
Set the maximum number of raster datasets that can be displayed at a given
time in a mosaic dataset.
Cell Size Tolerance
Factor (optional)
Consider images of similar spatial resolutions as having the same nominal
resolution. For example, with a factor of 0.1, all images with cell sizes within
10 percent of each other will be grouped together for tools and operations that
use cell sizes.
Output Cell Size
(optional)
Set the cell size of the mosaic dataset using an existing raster dataset or
specify its width (x) and height (y).
Metadata Level
(optional)
Set the level of metadata to expose from the server to a client when
publishing the mosaic dataset.
- FULL—Transmit metadata about processing applied at the mosaic dataset level
as well as metadata related to the individual raster datasets.
- NONE—No metadata will be exposed to the client.
- BASIC—Transmit metadata related to individual raster datasets, such as the
number of columns and rows, cell size, and spatial reference information.
Allowed Transmission
Field (optional)
Limit the fields in the attribute table that clients can view. By default,
the list includes:
- Name
- MinPS
- MaxPS
- LowPS
- HighPS
- Tag
- GroupName
- ProductName
- CenterX
- CenterY
- ZOrder
- Shape_Length
- Shape_Area
Use
Time (optional)
Enable animation through time on the mosaic dataset. If time is activated,
you need to specify the start and end fields, and the time format.
- Unchecked—The mosaic dataset will not be time aware. This is the default.
- Checked—The mosaic dataset will be time aware. This allows the client to use
the Time Slider.
Start Time Field
(optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the start time.
End
Time Field (optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the end time.
Time Format
(optional)
Select the format that represents time in the fields chosen above.
- YYYY—Year
- YYYYMM—Year and month
- YYYY/MM—Year and month
- YYYY-MM—Year and month
- YYYYMMDD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY/MM/DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY-MM-DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction of
seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
Geographic
Transformation (optional)
The geographic transformations to associate with this mosaic
dataset.
Max
Number of Download Items (optional)
Limit the number of raster datasets that can be downloaded per
request.
Max
Number of Records Returned (optional)
Limit the number of records that can be downloaded per request.
Minimum Pixel
Contribution (optional)
Set the minimum number of pixels required for a mosaic dataset item to be
considered significant enough to be used in the mosaic dataset. Because of
overlapping imagery, you may have an item that is displaying a small sliver of
its overall image. Skipping these mosaic dataset items will help the performance
of the mosaic dataset.
Time Interval
(optional)
Specify the duration that represents each time step interval. The time step
interval defines the granularity of the temporal data. The unit of time is
specified in the Time Interval Units parameter.
Time Interval Units
(optional)
Choose the appropriate units for your time interval.
- None—There is no time unit, or the units are unknown.
- Milliseconds—The time units are in milliseconds.
- Seconds—The time units are in seconds.
- Minutes—The time units are in minutes.
- Hours—The time units are in hours.
- Days—The time units are in days.
- Weeks—The time units are in weeks.
- Months—The time units are in months.
- Years—The time units are in years.
- Decades—The time units are in decades.
25. Mosaic Operator (optional)
Define rules for resolving overlapping pixels.
- FIRST—Display the first image within the attribute table.
- LAST—Display the last image within the attribute table.
- MIN—Display the lowest pixel values.
- MAX—Display the highest pixel values.
- MEAN—Use arithmetic mean to average overlapping pixels.
- BLEND—Use a distance weighted algorithm to average overlapping pixels.
- SUM—Add all of the overlapping pixel values.
Blend Width
(optional)
The number of pixels over which to apply the Blend Mosaic Operator.
View Point Spacing X
(optional)
When using the viewpoint mosaic method, you can horizontally shift the center
of the image using this parameter. The units are the same as the spatial
reference system.
View Point Spacing Y
(optional)
When using the viewpoint mosaic method, you can vertically shift the center
of the image using this parameter. The units are the same as the spatial
reference system.
Max
Number Per Mosaic (optional)
Set the maximum number of raster datasets that can be displayed at a given
time in a mosaic dataset.
Cell Size Tolerance
Factor (optional)
Consider images of similar spatial resolutions as having the same nominal
resolution. For example, with a factor of 0.1, all images with cell sizes within
10 percent of each other will be grouped together for tools and operations that
use cell sizes.
Output Cell Size
(optional)
Set the cell size of the mosaic dataset using an existing raster dataset or
specify its width (x) and height (y).
Metadata Level
(optional)
Set the level of metadata to expose from the server to a client when
publishing the mosaic dataset.
- FULL—Transmit metadata about processing applied at the mosaic dataset level
as well as metadata related to the individual raster datasets.
- NONE—No metadata will be exposed to the client.
- BASIC—Transmit metadata related to individual raster datasets, such as the
number of columns and rows, cell size, and spatial reference information.
Allowed Transmission
Field (optional)
Limit the fields in the attribute table that clients can view. By default,
the list includes:
- Name
- MinPS
- MaxPS
- LowPS
- HighPS
- Tag
- GroupName
- ProductName
- CenterX
- CenterY
- ZOrder
- Shape_Length
- Shape_Area
Use
Time (optional)
Enable animation through time on the mosaic dataset. If time is activated,
you need to specify the start and end fields, and the time format.
- Unchecked—The mosaic dataset will not be time aware. This is the default.
- Checked—The mosaic dataset will be time aware. This allows the client to use
the Time Slider.
Start Time Field
(optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the start time.
End
Time Field (optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the end time.
Time Format
(optional)
Select the format that represents time in the fields chosen above.
- YYYY—Year
- YYYYMM—Year and month
- YYYY/MM—Year and month
- YYYY-MM—Year and month
- YYYYMMDD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY/MM/DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY-MM-DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction of
seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
Geographic
Transformation (optional)
The geographic transformations to associate with this mosaic
dataset.
Max
Number of Download Items (optional)
Limit the number of raster datasets that can be downloaded per
request.
Max
Number of Records Returned (optional)
Limit the number of records that can be downloaded per request.
Minimum Pixel
Contribution (optional)
Set the minimum number of pixels required for a mosaic dataset item to be
considered significant enough to be used in the mosaic dataset. Because of
overlapping imagery, you may have an item that is displaying a small sliver of
its overall image. Skipping these mosaic dataset items will help the performance
of the mosaic dataset.
Time Interval
(optional)
Specify the duration that represents each time step interval. The time step
interval defines the granularity of the temporal data. The unit of time is
specified in the Time Interval Units parameter.
Time Interval Units
(optional)
Choose the appropriate units for your time interval.
- None—There is no time unit, or the units are unknown.
- Milliseconds—The time units are in milliseconds.
- Seconds—The time units are in seconds.
- Minutes—The time units are in minutes.
- Hours—The time units are in hours.
- Days—The time units are in days.
- Weeks—The time units are in weeks.
- Months—The time units are in months.
- Years—The time units are in years.
- Decades—The time units are in decades.
26.Blend Width (optional)
The number of pixels over which to apply the Blend Mosaic Operator.
27.View Point Spacing X (optional)
When using the viewpoint mosaic method, you can horizontally shift the center
of the image using this parameter. The units are the same as the spatial
reference system.
28.View Point Spacing Y (optional)
When using the viewpoint mosaic method, you can vertically shift the center of the image using this parameter. The units are the same as the spatial reference system.
29. Max Number Per Mosaic (optional)
Set the maximum number of raster datasets that can be displayed at a given
time in a mosaic dataset.
Cell Size Tolerance
Factor (optional)
Consider images of similar spatial resolutions as having the same nominal
resolution. For example, with a factor of 0.1, all images with cell sizes within
10 percent of each other will be grouped together for tools and operations that
use cell sizes.
Output Cell Size
(optional)
Set the cell size of the mosaic dataset using an existing raster dataset or
specify its width (x) and height (y).
Metadata Level
(optional)
Set the level of metadata to expose from the server to a client when
publishing the mosaic dataset.
- FULL—Transmit metadata about processing applied at the mosaic dataset level
as well as metadata related to the individual raster datasets.
- NONE—No metadata will be exposed to the client.
- BASIC—Transmit metadata related to individual raster datasets, such as the
number of columns and rows, cell size, and spatial reference information.
Allowed Transmission
Field (optional)
Limit the fields in the attribute table that clients can view. By default,
the list includes:
- Name
- MinPS
- MaxPS
- LowPS
- HighPS
- Tag
- GroupName
- ProductName
- CenterX
- CenterY
- ZOrder
- Shape_Length
- Shape_Area
Use
Time (optional)
Enable animation through time on the mosaic dataset. If time is activated,
you need to specify the start and end fields, and the time format.
- Unchecked—The mosaic dataset will not be time aware. This is the default.
- Checked—The mosaic dataset will be time aware. This allows the client to use
the Time Slider.
Start Time Field
(optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the start time.
End
Time Field (optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the end time.
Time Format
(optional)
Select the format that represents time in the fields chosen above.
- YYYY—Year
- YYYYMM—Year and month
- YYYY/MM—Year and month
- YYYY-MM—Year and month
- YYYYMMDD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY/MM/DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY-MM-DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction of
seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
Geographic
Transformation (optional)
The geographic transformations to associate with this mosaic
dataset.
Max
Number of Download Items (optional)
Limit the number of raster datasets that can be downloaded per
request.
Max
Number of Records Returned (optional)
Limit the number of records that can be downloaded per request.
Minimum Pixel
Contribution (optional)
Set the minimum number of pixels required for a mosaic dataset item to be
considered significant enough to be used in the mosaic dataset. Because of
overlapping imagery, you may have an item that is displaying a small sliver of
its overall image. Skipping these mosaic dataset items will help the performance
of the mosaic dataset.
Time Interval
(optional)
Specify the duration that represents each time step interval. The time step
interval defines the granularity of the temporal data. The unit of time is
specified in the Time Interval Units parameter.
Time Interval Units
(optional)
Choose the appropriate units for your time interval.
- None—There is no time unit, or the units are unknown.
- Milliseconds—The time units are in milliseconds.
- Seconds—The time units are in seconds.
- Minutes—The time units are in minutes.
- Hours—The time units are in hours.
- Days—The time units are in days.
- Weeks—The time units are in weeks.
- Months—The time units are in months.
- Years—The time units are in years.
- Decades—The time units are in decades.
30. Cell Size Tolerance Factor (optional)
Consider images of similar spatial resolutions as having the same nominal
resolution. For example, with a factor of 0.1, all images with cell sizes within
10 percent of each other will be grouped together for tools and operations that
use cell sizes.
Output Cell Size
(optional)
Set the cell size of the mosaic dataset using an existing raster dataset or
specify its width (x) and height (y).
Metadata Level
(optional)
Set the level of metadata to expose from the server to a client when
publishing the mosaic dataset.
- FULL—Transmit metadata about processing applied at the mosaic dataset level
as well as metadata related to the individual raster datasets.
- NONE—No metadata will be exposed to the client.
- BASIC—Transmit metadata related to individual raster datasets, such as the
number of columns and rows, cell size, and spatial reference information.
Allowed Transmission
Field (optional)
Limit the fields in the attribute table that clients can view. By default,
the list includes:
- Name
- MinPS
- MaxPS
- LowPS
- HighPS
- Tag
- GroupName
- ProductName
- CenterX
- CenterY
- ZOrder
- Shape_Length
- Shape_Area
Use
Time (optional)
Enable animation through time on the mosaic dataset. If time is activated,
you need to specify the start and end fields, and the time format.
- Unchecked—The mosaic dataset will not be time aware. This is the default.
- Checked—The mosaic dataset will be time aware. This allows the client to use
the Time Slider.
Start Time Field
(optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the start time.
End
Time Field (optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the end time.
Time Format
(optional)
Select the format that represents time in the fields chosen above.
- YYYY—Year
- YYYYMM—Year and month
- YYYY/MM—Year and month
- YYYY-MM—Year and month
- YYYYMMDD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY/MM/DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY-MM-DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction of
seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
Geographic
Transformation (optional)
The geographic transformations to associate with this mosaic
dataset.
Max
Number of Download Items (optional)
Limit the number of raster datasets that can be downloaded per
request.
Max
Number of Records Returned (optional)
Limit the number of records that can be downloaded per request.
Minimum Pixel
Contribution (optional)
Set the minimum number of pixels required for a mosaic dataset item to be
considered significant enough to be used in the mosaic dataset. Because of
overlapping imagery, you may have an item that is displaying a small sliver of
its overall image. Skipping these mosaic dataset items will help the performance
of the mosaic dataset.
Time Interval
(optional)
Specify the duration that represents each time step interval. The time step
interval defines the granularity of the temporal data. The unit of time is
specified in the Time Interval Units parameter.
Time Interval Units
(optional)
Choose the appropriate units for your time interval.
- None—There is no time unit, or the units are unknown.
- Milliseconds—The time units are in milliseconds.
- Seconds—The time units are in seconds.
- Minutes—The time units are in minutes.
- Hours—The time units are in hours.
- Days—The time units are in days.
- Weeks—The time units are in weeks.
- Months—The time units are in months.
- Years—The time units are in years.
- Decades—The time units are in decades.
31. Output Cell Size (optional)
Set the cell size of the mosaic dataset using an existing raster dataset or
specify its width (x) and height (y).
Metadata Level
(optional)
Set the level of metadata to expose from the server to a client when
publishing the mosaic dataset.
- FULL—Transmit metadata about processing applied at the mosaic dataset level
as well as metadata related to the individual raster datasets.
- NONE—No metadata will be exposed to the client.
- BASIC—Transmit metadata related to individual raster datasets, such as the
number of columns and rows, cell size, and spatial reference information.
Allowed Transmission
Field (optional)
Limit the fields in the attribute table that clients can view. By default,
the list includes:
- Name
- MinPS
- MaxPS
- LowPS
- HighPS
- Tag
- GroupName
- ProductName
- CenterX
- CenterY
- ZOrder
- Shape_Length
- Shape_Area
Use
Time (optional)
Enable animation through time on the mosaic dataset. If time is activated,
you need to specify the start and end fields, and the time format.
- Unchecked—The mosaic dataset will not be time aware. This is the default.
- Checked—The mosaic dataset will be time aware. This allows the client to use
the Time Slider.
Start Time Field
(optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the start time.
End
Time Field (optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the end time.
Time Format
(optional)
Select the format that represents time in the fields chosen above.
- YYYY—Year
- YYYYMM—Year and month
- YYYY/MM—Year and month
- YYYY-MM—Year and month
- YYYYMMDD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY/MM/DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY-MM-DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction of
seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
Geographic
Transformation (optional)
The geographic transformations to associate with this mosaic
dataset.
Max
Number of Download Items (optional)
Limit the number of raster datasets that can be downloaded per
request.
Max
Number of Records Returned (optional)
Limit the number of records that can be downloaded per request.
Minimum Pixel
Contribution (optional)
Set the minimum number of pixels required for a mosaic dataset item to be
considered significant enough to be used in the mosaic dataset. Because of
overlapping imagery,
you may have an item that is displaying a small sliver of
its overall image. Skipping these mosaic dataset items will help the performance
of the mosaic dataset.
Time Interval
(optional)
Specify the duration that represents each time step interval. The time step
interval defines the granularity of the temporal data. The unit of time is
specified in the Time Interval Units parameter.
Time Interval Units
(optional)
Choose the appropriate units for your time interval.
- None—There is no time unit, or the units are unknown.
- Milliseconds—The time units are in milliseconds.
- Seconds—The time units are in seconds.
- Minutes—The time units are in minutes.
- Hours—The time units are in hours.
- Days—The time units are in days.
- Weeks—The time units are in weeks.
- Months—The time units are in months.
- Years—The time units are in years.
- Decades—The time units are in decades.
32. Metadata Level (optional)
Set the level of metadata to expose from the server to a client when
publishing the mosaic dataset.
-
FULL—Transmit metadata about processing applied at the mosaic dataset level
as well as metadata related to the individual raster datasets.
- NONE—No metadata will be exposed to the client.
- BASIC—Transmit metadata related to individual raster datasets, such as the
number of columns and rows, cell size, and spatial reference information.
Allowed Transmission
Field (optional)
Limit the fields in the attribute table that clients can view. By default,
the list includes:
- Name
- MinPS
- MaxPS
- LowPS
- HighPS
- Tag
- GroupName
- ProductName
- CenterX
- CenterY
- ZOrder
- Shape_Length
- Shape_Area
Use
Time (optional)
Enable animation through time on the mosaic dataset. If time is activated,
you need to specify the start and end fields, and the time format.
- Unchecked—The mosaic dataset will not be time aware. This is the default.
- Checked—The mosaic dataset will be time aware. This allows the client to use
the Time Slider.
Start Time Field
(optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the start time.
End
Time Field (optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the end time.
Time Format
(optional)
Select the format that represents time in the fields chosen above.
- YYYY—Year
- YYYYMM—Year and month
- YYYY/MM—Year and month
- YYYY-MM—Year and month
- YYYYMMDD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY/MM/DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY-MM-DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction of
seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
Geographic
Transformation (optional)
The geographic transformations to associate with this mosaic
dataset.
Max
Number of Download Items (optional)
Limit the number of raster datasets that can be downloaded per
request.
Max
Number of Records Returned (optional)
Limit the number of records that can be downloaded per request.
Minimum Pixel
Contribution (optional)
Set the minimum number of pixels required for a mosaic dataset item to be
considered significant enough to be used in the mosaic dataset. Because of
overlapping imagery, you may have an item that is displaying a small sliver of
its overall image. Skipping these mosaic dataset items will help the performance
of the mosaic dataset.
Time Interval
(optional)
Specify the duration that represents each time step interval. The time step
interval defines the granularity of the temporal data. The unit of time is
specified in the Time Interval Units parameter.
Time Interval Units
(optional)
Choose the appropriate units for your time interval.
- None—There is no time unit, or the units are unknown.
- Milliseconds—The time units are in milliseconds.
- Seconds—The time units are in seconds.
- Minutes—The time units are in minutes.
- Hours—The time units are in hours.
- Days—The time units are in days.
- Weeks—The time units are in weeks.
- Months—The time units are in months.
- Years—The time units are in years.
- Decades—The time units are in decades.
33. Allowed Transmission Field (optional)
Limit the fields in the attribute table that clients can view. By default,
the list includes:
- Name
- MinPS
- MaxPS
- LowPS
- HighPS
- Tag
- GroupName
- ProductName
- CenterX
- CenterY
- ZOrder
- Shape_Length
- Shape_Area
35. Start Time Field (optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the start time.
36. End Time Field (optional)
The field from the attribute table that shows the end time.
37. Time Format (optional)
Select the format that represents time in the fields chosen above.
- YYYY—Year
- YYYYMM—Year and month
- YYYY/MM—Year and month
- YYYY-MM—Year and month
- YYYYMMDD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY/MM/DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYY-MM-DD—Year, month, and day
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss—Year, month, day, hour, minute, and seconds
- YYYYMMDDhhmmss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction of
seconds
- YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
- YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.s—Year, month, day, hour, minute, seconds, and fraction
of seconds
Geographic
Transformation (optional)
The geographic transformations to associate with this mosaic
dataset.
Max
Number of Download Items (optional)
Limit the number of raster datasets that can be downloaded per
request.
Max
Number of Records Returned (optional)
Limit the number of records that can be downloaded per request.
Minimum Pixel
Contribution (optional)
Set the minimum number of pixels required for a mosaic dataset item to be
considered significant enough to be used in the mosaic dataset. Because of
overlapping imagery, you may have an item that is displaying a small sliver of
its overall image. Skipping these mosaic dataset items will help the performance
of the mosaic dataset.
Time Interval
(optional)
Specify the duration that represents each time step interval. The time step
interval defines the granularity of the temporal data. The unit of time is
specified in the Time Interval Units parameter.
Time Interval Units
(optional)
Choose the appropriate units for your time interval.
- None—There is no time unit, or the units are unknown.
- Milliseconds—The time units are in milliseconds.
- Seconds—The time units are in seconds.
- Minutes—The time units are in minutes.
- Hours—The time units are in hours.
- Days—The time units are in days.
- Weeks—The time units are in weeks.
- Months—The time units are in months.
- Years—The time units are in years.
- Decades—The time units are in decades.
38. Geographic Transformation (optional)
The geographic transformations to associate with this mosaic dataset.
39. Max Number of Download Items (optional)
Limit the number of raster datasets that can be downloaded per request.
40. Max Number of Records Returned (optional)
Limit the number of records that can be downloaded per request.
41. Minimum Pixel Contribution (optional)
Set the minimum number of pixels required for a mosaic dataset item to be
considered significant enough to be used in the mosaic dataset. Because of
overlapping imagery, you may have an item that is displaying a small sliver of
its overall image. Skipping these mosaic dataset items will help the performance
of the mosaic dataset.
42. Time Interval (optional)
Specify the duration that represents each time step interval. The time step
interval defines the granularity of the temporal data. The unit of time is
specified in the Time Interval Units parameter.
43. Time Interval Units (optional)
Choose the appropriate units for your time interval.
- None—There is no time unit, or the units are unknown.
- Milliseconds—The time units are in milliseconds.
- Seconds—The time units are in seconds.
- Minutes—The time units are in minutes.
- Hours—The time units are in hours.
- Days—The time units are in days.
- Weeks—The time units are in weeks.
- Months—The time units are in months.
- Years—The time units are in years.
- Decades—The time units are in decades.
- Centuries—The time units are in centuries.


Comments
Post a Comment