Tabulate Area, Zonal Fill, Zonal Geometry and as Table, Zonal Histogram, Statistics and Statistics as Table Tools
Tabulate Area
How to use Tabulate Area Tool in Arc Toolbox??
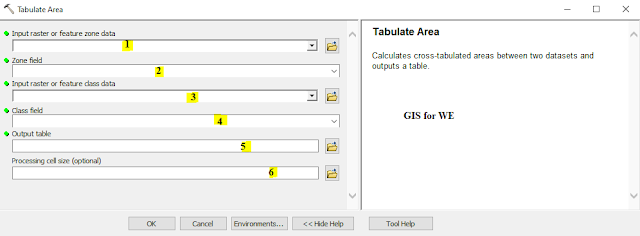 |
| Tabulate Area |
Path to access the tool
:
Tabulate
Area Tool, Zonal Toolset, Spatial Analyst Tools Toolbox
Tabulate Area
Calculates
cross-tabulated areas between two datasets and outputs a table.
1. Input raster or feature zone data
Dataset that defines the
zones.
The zones can be defined
by an integer raster or a feature layer.
2. Zone field
Field that holds the
values that define each zone.
It can be an integer or
a string field of the zone dataset.
3. Input raster or feature class data
The dataset that defines
the classes that will have their area summarized within each zone.
The class input can be
an integer raster layer or a feature layer.
4. Class field
The field that holds the
class values.
It can be an integer or
a string field of the input class data.
5. Output table
Output table that will
contain the summary of the area of each class in each zone.
The format of the table
is determined by the output location and path. By default, the output will be a
geodatabase table. If the path is not in a geodatabase, the format is
determined by the extension. If the extension is .dbf, it will be in dBASE
format. If no extension is specified,
the output will be an INFO table.
6. Processing cell size (optional)
The cell size of the
output raster that will be created.
This parameter can be
defined by a numeric value or obtained from an existing raster dataset. If the
cell size hasn't been explicitly specified as the parameter value, the
environment cell size value will be used if specified; otherwise, additional
rules will be used to calculate it from the other inputs. See the usage for
more detail.
Zonal Fill
How to use Zonal Fill Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
| Zonal Fill |
Path to access the tool
:
Zonal
Fill Tool, Zonal Toolset, Spatial Analyst Tools Toolbox
Zonal Fill
Fills zones using the
minimum cell value from a weight raster along the zone boundary.
1. Input zone raster
The input raster that
defines the zones to be filled.
2. Input weight raster
Weight, or value, to be
assigned to each zone.
3. Output raster
The output raster for
which the zones have been filled.
Zonal Geometry
How to use Zonal Geometry Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
| Zonal Geometry |
Path to access the tool
:
Zonal
Geometry Tool, Zonal Toolset, Spatial Analyst Tools Toolbox
Zonal Geometry
Calculates the specified
geometry measure (area, perimeter, thickness, or the characteristics of
ellipse) for each zone in a dataset.
1. Input raster or feature zone data
Dataset that defines the
zones.
The zones can be defined
by an integer raster or a feature layer.
2. Zone field
Field that holds the
values that define each zone.
It must be an integer
field of the zone dataset.
3. Output raster
The output zonal
geometry raster.
4. Geometry type (optional)
Geometry type to be calculated.
- AREA—The area for each zone.
- PERIMETER—The perimeter for each zone.
- THICKNESS—The deepest (or thickest) point within the zone from its surrounding cells.
- CENTROID—Locates the centroids of each zone.
5. Output cell size (optional)
The cell size of the
output raster that will be created.
This parameter can be
defined by a numeric value or obtained from an existing raster dataset. If the
cell size hasn't been explicitly specified as the parameter value, the
environment cell size value will be used if specified; otherwise,
additional
rules will be used to calculate it from the other inputs. See the usage for
more detail.
Zonal Geometry as Table
How to use Zonal Geometry as Table Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
| Zonal Geometry as Table |
Path to access the tool
:
Zonal
Geometry as Table Tool, Zonal Toolset, Spatial
Analyst Tools Toolbox
Zonal Geometry as Table
Calculates the geometry
measures (area, perimeter, thickness, and the characteristics of ellipse) for
each zone in a dataset and reports the results as a table.
1. Input raster or feature zone data
Dataset that defines the
zones.
The zones can be defined
by an integer raster or a feature layer.
2. Zone field
Field that holds the
values that define each zone.
It must be an integer
field of the zone dataset.
3. Output table
Output table that will
contain the summary of the values in each zone.
The format of the table
is determined by the output location and path. By default, the output will be a
geodatabase table. If the path is not in a geodatabase, the format is
determined by the extension. If the extension is .dbf, it will be in dBASE
format. If no extension is specified, the output will be an INFO table.
4. Processing cell size (optional)
The cell size of the
output raster that will be created.
This parameter can be
defined by a numeric value or obtained from an existing raster dataset. If the
cell size hasn't been explicitly specified as the parameter value, the
environment cell size value will be used if specified; otherwise, additional
rules will be used to calculate it from the other inputs. See the usage for
more detail.
Zonal Histogram
How to use Zonal Histogram Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
| Zonal Histogram |
Path to access the tool
:
Zonal
Histogram Tool, Zonal Toolset, Spatial Analyst Tools Toolbox
Zonal Histogram
Creates a table and a
histogram graph that show the frequency distribution of cell values on the
Value input for each unique Zone.
1. Input raster or feature zone data
Dataset that defines the
zones.
The zones can be defined
by an integer raster or a feature layer.
2. Zone field
Field that holds the
values that define each zone.
It can be an integer or
a string field of the zone dataset.
3. Input value raster
The raster values to
create the histograms.
4. Output table
The output table file.
The format of the table
is determined by the output location and path. By default, the output will be a
geodatabase table. If the path is not in a geodatabase, the format is
determined by the extension. If the extension is .dbf, it will be in dBASE
format. If no extension is specified, the output will be an INFO table.
The optional graph
output is created from the information in the table.
5. Output graph name (optional)
The name of the output
graph for display.
The graph is temporary.
To persist it, use the Save Graph tool.
Zonal Statistics
How to use Zonal Statistics Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
| Zonal Statistics |
Path to access the tool
:
Zonal
Statistics Tool, Zonal Toolset, Spatial
Analyst Tools Toolbox
Zonal Statistics
Calculates statistics on
values of a raster within the zones of another dataset.
1. Input raster or feature zone data
Dataset that defines the
zones.
The zones can be defined
by an integer raster or a feature layer.
2. Zone field
Field that holds the
values that define each zone.
It can be an integer or
a string field of the zone dataset.
3. Input value raster
Raster that contains the
values on which to calculate a statistic.
4. Output raster
The output zonal
statistics raster.
5. Statistics type (optional)
Statistic type to be calculated.
- MEAN—Calculates the average of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- MAJORITY—Determines the value that occurs most often of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- MAXIMUM—Determines the largest value of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- MEDIAN—Determines the median value of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- MINIMUM—Determines the smallest value of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- MINORITY—Determines the value that occurs least often of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- RANGE—Calculates the difference between the largest and smallest value of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- STD—Calculates the standard deviation of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- SUM—Calculates the total value of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- VARIETY—Calculates the number of unique values for all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
6. Ignore NoData in calculations (optional)
Denotes whether NoData values in the Value input will influence the results of the zone that they fall within.
Checked—Within any particular zone, only cells that have a value in the input Value raster will be used in determining the output value for that zone. NoData cells in the Value raster will be ignored in the statistic calculation. This is the default.
Unchecked—Within any particular zone, if any NoData cells exist in the Value raster, it is deemed that there is insufficient information to perform statistical calculations for all the cells in that zone; therefore, the entire zone will receive the NoData value on the output raster.
Zonal Statistics as Table
How to use Zonal Statistics as Table Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
| Zonal Statistics as Table |
Path to access the tool
:
Zonal
Statistics as Table Tool, Zonal Toolset, Spatial
Analyst Tools Toolbox
Zonal Statistics as Table
Summarizes the values of
a raster within the zones of another dataset and reports the results to a
table.
1. Input raster or feature zone data
Dataset that defines the
zones.
The zones can be defined
by an integer raster or a feature layer.
2. Zone field
Field that holds the
values that define each zone.
It can be an integer or
a string field of the zone dataset.
3. Input value raster
Raster that contains the
values on which to calculate a statistic.
4. Output table
Output table that will contain
the summary of the values in each zone.
The format of the table
is determined by the output location and path. By default, the output will be a
geodatabase table. If the path is not in a geodatabase, the format is
determined by the extension. If the extension is .dbf, it will be in dBASE
format. If no extension is specified, the output will be an INFO table.
5. Ignore NoData in calculations (optional)
Denotes whether NoData values in the Value input will influence the results of the zone that they fall within.
- Checked—Within any particular zone, only cells that have a value in the input Value raster will be used in determining the output value for that zone. NoData cells in the Value raster will be ignored in the statistic calculation. This is the default.
- Unchecked—Within any particular zone, if any NoData cells exist in the Value raster, it is deemed that there is insufficient information to perform statistical calculations for all the cells in that zone; therefore, the entire zone will receive the NoData value on the output raster.
6. Statistics type (optional)
Statistic type to be calculated.
- ALL—All of the statistics will be calculated. This is the default.
- MEAN—Calculates the average of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- MAJORITY—Determines the value that occurs most often of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- MAXIMUM—Determines the largest value of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- MEDIAN—Determines the median value of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- MINIMUM—Determines the smallest value of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- MINORITY—Determines the value that occurs least often of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- RANGE—Calculates the difference between the largest and smallest value of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- STD—Calculates the standard deviation of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- SUM—Calculates the total value of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- VARIETY—Calculates the number of unique values for all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- MIN_MAX—Both the minimum and maximum statistics are calculated.
- MEAN_STD—Both the mean and standard deviation statistics are calculated.
- MIN_MAX_MEAN—The minimum, maximum and mean statistics are calculated.

Comments
Post a Comment