Sink, Snap Pour Point, Stream Link and Order and to Feature, Watershed Tools
Sink
How to use Sink Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
| Sink Tool |
Path to access the tool
:
Sink Tool, Hydrology Toolset, Spatial Analyst Tools Toolbox
Sink
Creates a raster
identifying all sinks or areas of internal drainage.
1. Input flow direction raster
The input raster that
shows the direction of flow out of each cell.
The flow direction raster
can be created using the Flow Direction tool, run using the default flow
direction type D8.
2. Output raster
The output raster that
shows all the sinks (areas of internal drainage) on the input surface.
This output is of
integer type.
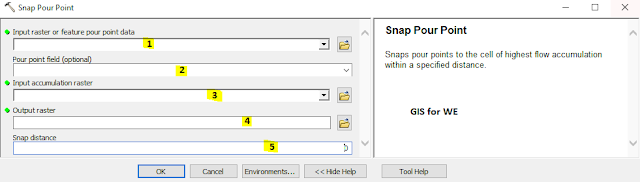
Snap Pour Point
How to use Snap Pour Point Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
| Snap Pour Point |
Path to access the tool
:
Snap
Pour Point Tool, Hydrology Toolset, Spatial
Analyst Tools Toolbox
Snap Pour Point
Snaps pour points to the
cell of highest flow accumulation within a specified distance.
1. Input raster or feature pour point data
The input pour point
locations that are to be snapped.
For a raster input, all
cells that are not NoData (that is, have a value) will be considered pour
points and will be snapped.
For a point feature
input, this specifies the locations of cells that will be snapped.
2. Pour point field (optional)
Field used to assign
values to the pour point locations.
If the pour point
dataset is a raster, use Value.
If the pour point
dataset is a feature, use a numeric field. If the field contains floating-point
values, they will be truncated into integers.
3. Input accumulation raster
The input flow
accumulation raster.
This can be created with
the Flow Accumulation tool.
4. Output raster
The output pour point
raster where the original pour point locations have been snapped to locations
of higher accumulated flow.
This output is of
integer type.
5. Snap distance
Maximum distance, in map
units, to search for a cell of higher accumulated flow.
Stream Link
How to use Stream Link Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
| Stream Link |
Path to access the tool
:
Stream
Link Tool, Hydrology Toolset, Spatial Analyst Tools Toolbox
Stream Link
Assigns unique values to
sections of a raster linear network between intersections.
1. Input stream raster
An input raster that
represents a linear stream network.
2. Input flow direction raster
The input raster that
shows the direction of flow out of each cell.
The flow direction
raster can be created using the Flow Direction tool, run using the default flow
direction type D8.
3. Output raster
The output stream link
raster.
This output is of
integer type.
Stream Order
How to use Stream Order Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
| Stream Order |
Path to access the tool
:
Stream
Order Tool, Hydrology Toolset, Spatial Analyst Tools Toolbox
Stream Order
Assigns a numeric order
to segments of a raster representing branches of a linear network.
1. Input stream raster
An input raster that
represents a linear stream network.
The input stream raster
linear network should be represented as values greater than or equal to one on
a background of NoData.
2. Input flow direction raster
The input raster that
shows the direction of flow out of each cell.
The flow direction
raster can be created using the Flow Direction tool, run using the default flow
direction type D8.
3. Output raster
The output stream order
raster.
This output is of
integer type.
4. Method of stream ordering (optional)
The method used for assigning stream order.
- STRAHLER—The method of stream ordering proposed by Strahler in 1952. Stream order only increases when streams of the same order intersect. Therefore, the intersection of a first-order and second-order link will remain a second-order link, rather than creating a third-order link. This is the default.
- SHREVE—The method of stream ordering by magnitude, proposed by Shreve in 1967. All links with no tributaries are assigned a magnitude (order) of one. Magnitudes are additive downslope. When two links intersect, their magnitudes are added and assigned to the downslope link.
Stream to Feature
How to use Stream to Feature Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
| Stream to Feature |
Path to access the tool
:
Stream
to Feature Tool, Hydrology Toolset, Spatial
Analyst Tools Toolbox
Stream to Feature
Converts a raster
representing a linear network to features representing the linear network.
1. Input stream raster
An input raster that
represents a linear stream network.
2. Input flow direction raster
The input raster that
shows the direction of flow out of each cell.
The flow direction
raster can be created using the Flow Direction tool.
3. Output polyline features
Output feature class
that will hold the converted streams.
4. Simplify polylines (optional)
Specifies whether weeding is used.
- Checked—The feature is weeded to reduce the number of vertices. The Douglas-Puecker algorithm for line generalization is used with a tolerance of sqrt(0.5) * cell size.
- Unchecked—No weeding is applied.
By default, weeding is
applied.
Watershed
How to use Watershed Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
| Watershed Tool |
Path to access the tool
:
Watershed Tool, Hydrology Toolset, Spatial Analyst Tools Toolbox
Watershed
Determines the
contributing area above a set of cells in a raster.
1. Input flow direction raster
The input raster that
shows the direction of flow out of each cell.
The flow direction
raster can be created using the Flow Direction tool, run using the default flow
direction type D8.
2. Input raster or feature pour point data
The input pour point
locations.
For a raster, this
represents cells above which the contributing area, or catchment, will be
determined. All cells that are not NoData will be used as source cells.
For a point feature
dataset, this represents locations above which the contributing area, or
catchment, will be determined.
3. Pour point field (optional)
Field used to assign
values to the pour point locations.
If the pour point
dataset is a raster, use Value.
If the pour point
dataset is a feature, use a numeric field. If the field contains floating-point
values, they will be truncated into integers.
4. Output raster
The output raster that
shows the contributing area.
This output is of integer type.

Comments
Post a Comment