Basin, Fill, Flow Accumulation and Direction and Distance and Length Tools
Basin
How to use Basin Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
| Basin Tool |
Path to access the tool
:
Basin Tool, Hydrology Toolset, Spatial Analyst Tools Toolbox
Basin
Creates a raster delineating
all drainage basins.
1. Input flow direction raster
The input raster that
shows the direction of flow out of each cell.
A flow direction raster
can be created with the Flow Direction tool, using the default D8 flow
direction type.
2. Output raster
The output raster that
delineates the drainage basins.
This output is of
integer type.
Fill
How to use Fill Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
| Fill Tool |
Path to access the tool
:
Fill Tool, Hydrology Toolset, Spatial Analyst Tools Toolbox
Fill
Fills sinks in a surface
raster to remove small imperfections in the data.
1. Input surface raster
The input raster
representing a continuous surface.
2. Output surface raster
The output surface
raster after the sinks have been filled.
If the surface raster is
integer, the output filled raster will be integer type.
If the input is
floating point, the output raster will be floating point.
3. Z limit (optional)
Maximum elevation
difference between a sink and its pour point to be filled.
If the difference in
z-values between a sink and its pour point is greater than the z_limit, that
sink will not be filled.
The value for z-limit
must be greater than zero.
Unless a value is
specified for this parameter, all sinks will be filled, regardless of depth.
Flow Accumulation
How to use Flow Accumulation Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
| Flow Accumulation |
Path to access the tool
:
Flow
Accumulation Tool, Hydrology Toolset, Spatial
Analyst Tools Toolbox
Flow Accumulation
Creates a raster of
accumulated flow into each cell. A weight factor can optionally be applied.
1. Input flow direction raster
The input raster that
shows the direction of flow out of each cell.
The flow direction
raster can be created using the Flow Direction tool.
The flow direction
raster can be created using D8, Multiple Flow Direction (MFD) and D-Infinity
methods. Use the Input flow direction type parameter to specify which method
was used when the flow direction raster was created.
2. Output accumulation raster
The output raster that
shows the accumulated flow to each cell.
3. Input weight raster (optional)
An optional input raster
for applying a weight to each cell.
If no weight raster is
specified, a default weight of 1 will be applied to each cell. For each cell in
the output raster, the result will be the number of cells that flow into it.
4. Output data type (optional)
The output accumulation raster can be integer, floating point, or double type.
- FLOAT—The output raster will be floating point type. This is the default.
- INTEGER—The output raster will be integer type.
- DOUBLE—The output raster will be double type.
5. Flow direction type (optional)
The input flow direction raster can be of type D8, Multi Flow Direction (MFD) or D-Infinity (DINF).
- D8—The input flow direction raster is of type D8. This is the default.
- MFD—The input flow direction raster is of type Multi Flow Direction (MFD).
- DINF—The input flow direction raster is of type D-Infinity (DINF).
Flow Direction
How to use Flow Direction Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
Flow Direction |
Path to access the tool
:
Flow
Direction Tool, Hydrology Toolset, Spatial Analyst Tools Toolbox
Flow Direction
Creates a raster of flow
direction from each cell to its downslope neighbor, or neighbors, using D8,
Multiple Flow Direction (MFD) or D-Infinity (DINF) methods.
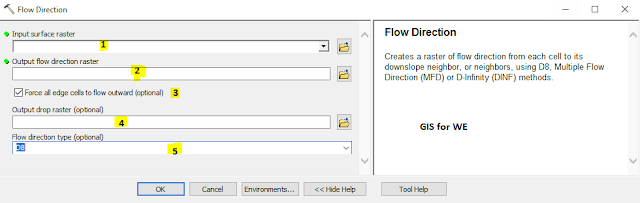
1. Input surface raster
The input raster
representing a continuous surface.
2. Output flow direction raster
The output raster that
shows the flow direction from each cell to its downslope neighbor(s) using D8,
Multiple Flow Direction (MFD) or D-Infinity (DINF) methods.
This output is of
integer type.
3. Force all edge cells to flow outward (optional)
Specifies if edge cells will always flow outward or follow normal flow rules.
- Unchecked—If the maximum drop on the inside of an edge cell is greater than zero, the flow direction will be determined as usual; otherwise, the flow direction will be toward the edge. Cells that should flow from the edge of the surface raster inward will do so. This is the default.
- Checked—All cells at the edge of the surface raster will flow outward from the surface raster.
4. Output drop raster (optional)
An optional output drop
raster.
The drop raster returns
the ratio of the maximum change in elevation from each cell along the direction
of flow to the path length between centers of cells, expressed in percentages.
This output is of
floating-point type.
5. Flow direction type (optional)
Specifies the type of flow method to use while computing flow directions.
- D8—Assign a flow direction based on the D8 flow method. This method assigns flow direction to the steepest downslope neighbor. This is the default.
- MFD—Assign a flow direction based on the MFD flow method. This method assigns multiple flow directions towards all downslope neighbors.
- DINF—Assign a flow direction based on the D-Infinity flow method using the steepest slope of a triangular facet.
Flow Distance
How to use Flow Distance Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
| Flow Distance |
Path to access the tool
:
Flow
Distance Tool, Hydrology Toolset, Spatial Analyst Tools Toolbox
Flow Distance
Computes, for each cell,
the horizontal or vertical component of downslope distance, following the flow
path(s), to cell(s) on a stream into which they flow. In case of multiple flow
paths, minimum, weighted mean, or maximum flow distance can be computed.
If an optional flow
direction raster is provided, the down slope direction(s) will be limited to
those defined by the input flow direction raster.
1. Input stream raster
An input stream raster
that represents a linear stream network.
2. Input surface raster
The input raster
representing a continuous surface.
The output flow distance raster.
4. Input flow direction raster (optional)
The input raster that
shows the direction of flow out of each cell.
When a flow direction
raster is provided, the down slope direction(s) will be limited to those
defined by the input flow directions.
The flow direction
raster can be created using the Flow Direction tool.
The flow direction
raster can be created using D8, Multiple Flow Direction (MFD) and D-Infinity
methods. Use the Input flow direction type parameter to specify which method
was used when the flow direction raster was created.
5. Distance type (optional)
Determines if the vertical or horizontal component of flow distance is calculated.
- VERTICAL—The flow distance calculations represent the vertical component of flow distance, following the flow path, from each cell in the domain to cell(s) on the stream into which they flow. This is the default.
- HORIZONTAL—The flow distance calculations represent the horizontal component of flow distance, following the flow path, from each cell in the domain to cell(s) on the stream into which they flow.
6. Flow direction type (optional)
The input flow direction raster can be of type D8, Multi Flow Direction (MFD) or D-Infinity (DINF).
- D8—The input flow direction raster is of type D8. This is the default.
- MFD—The input flow direction raster is of type Multi Flow Direction (MFD).
- DINF—The input flow direction raster is of type D-Infinity (DINF).
7. Statistics Type (optional)
Determines the statistics type used to compute flow distance over multiple flow paths. If there is only a single flow path from each cell to a cell on the stream, all statistics types produce the same result.
- MINIMUM—Where multiple flow paths exist, minimum flow distance in computed. This is the default.
- WEIGHTED_MEAN—Where multiple flow paths exist, a weighted mean of flow distance is computed. Flow proportion from a cell to its downstream neighboring cells are used as weights for computing weighted mean.
- MAXIMUM—When multiple flow paths exist, maximum flow distance is computed.
Flow Length
How to use Flow Length Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
| Flow Length |
Path to access the tool
:
Flow
Length Tool, Hydrology Toolset, Spatial Analyst Tools Toolbox
Flow Length
Calculates the upstream
or downstream distance, or weighted distance,
along the flow path for each
cell.
1. Input flow direction raster
The input raster that
shows the direction of flow out of each cell.
The flow direction
raster can be created using the Flow Direction tool.
2. Output raster
The output raster that
shows for each cell the upstream or downstream distance along a flow path.
3. Direction of measurement (optional)
The direction of measurement along the flow path.
- DOWNSTREAM—Calculates the downslope distance along the flow path, from each cell to a sink or outlet on the edge of the raster.
- UPSTREAM—Calculates the longest upslope distance along the flow path, from each cell to the top of the drainage divide.
4. Input weight raster (optional)
An optional input raster
for applying a weight to each cell.
If no weight raster is specified, a default weight of 1 will be applied to each cell. For each cell in the output raster, the result will be the number of cells that flow into it.

Comments
Post a Comment