Classify Raster, Compute Confusion Matrix and Segment Attributes, Create Accuracy Assessment Points Tools
Classify Raster
How to use Classify Raster Tool
in Arc Toolbox??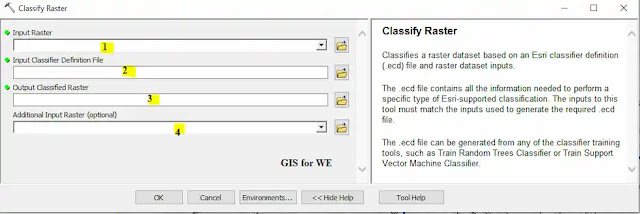
Classify Raster
Path to access the tool
:
Classify
Raster Tool, Segmentation and Classification Toolset, Spatial Analyst
Tools Toolbox
Classify Raster
Classifies a raster
dataset based on an Esri classifier definition (.ecd) file and raster dataset
inputs.
The .ecd file contains
all the information needed to perform a specific type of Esri-supported
classification. The inputs to this tool must match the inputs used to generate
the required .ecd file.
The .ecd file can be
generated from any of the classifier training tools, such as Train Random Trees
Classifier or Train Support Vector Machine Classifier.
1. Input Raster
The raster dataset to
classify.
2. Input Classifier Definition File
The input Esri
classifier definition (.ecd) file containing the statistics on the chosen
attributes for the classifier.
3. Output Classified Raster
The path and name of the
classified image you are creating.
The output classified
raster is defined by the input raster dataset and .ecd file inputs.
4. Additional Input Raster (optional)
Incorporate ancillary
raster datasets, such as a multispectral image or a DEM, to generate attributes
and other required information for the classifier.
This raster will be needed
when calculating attributes such as mean or standard deviation. This parameter
is optional.
Compute Confusion Matrix
How to use Compute
Confusion Matrix Tool in Arc Toolbox??
Compute Confusion Matrix
Path to access the tool
:
Compute
Confusion Matrix Tool, Segmentation and
Classification Toolset, Spatial Analyst Tools Toolbox
Compute Confusion Matrix
Computes a confusion
matrix with errors of omission and commission and derives a kappa index of
agreement and an overall accuracy between the classified map and the reference
data.
This tool uses the
outputs from the Create Accuracy Assessment Points tool or the Update Accuracy
Assessment Points tool.
1. Input Accuracy Assessment Points
The accuracy assessment
point feature class, created from the Create Accuracy Assessment Points tool, containing
the CLASSIFIED and GROUND_TRUTH fields.
2. Output Confusion Matrix
The output file name of
the confusion matrix in table format.
The format of the table
is determined by the output location and path. By default, the output will be a
geodatabase table. If the path is not in a geodatabase, specify a .dbf extension
to save it in dBASE format.
Compute Segment Attributes
How to use Compute Segment
Attributes Tool in Arc Toolbox??
Compute Segment Attributes
Path to access the tool
:
Compute
Segment Attributes Tool, Segmentation and
Classification Toolset, Spatial Analyst Tools Toolbox
Compute Segment Attributes
Computes a set of
attributes associated with the segmented image. The input raster can be a
single-band or 3-band, 8-bit segmented image.
1. Input Segmented RGB Or Gray Raster
The input segmented
raster dataset, where all the pixels belonging to a segment have the same
converged RGB color. Usually, it is an 8-bit, 3-band RGB raster, but it can
also be a 1-band grayscale raster.
2. Output Segment Index Raster
The output segment index
raster, where the attributes for each segment are recorded in the associated
attribute table.
3. Additional Input Raster (optional)
Incorporate ancillary
raster datasets, such as a multispectral image or a DEM, to generate attributes
and other required information for the classifier. This raster will be needed
when calculating attributes such as mean or standard deviation. This parameter
is optional.
4. Segment Attributes Used (optional)
Specifies the attributes to be included in the attribute table associated with the output raster.
- COLOR—The RGB color values are derived from the input raster, on a per-segment basis.
- MEAN—The average digital number (DN), derived from the optional pixel image, on a per-segment basis.
- STD—The standard deviation, derived from the optional pixel image, on a per-segment basis.
- COUNT—The number of pixels comprising the segment, on a per-segment basis.
- COMPACTNESS—The degree to which a segment is compact or circular, on a per-segment basis. The values range from 0 to 1, where 1 is a circle.
- RECTANGULARITY—The degree to which the segment is rectangular, on a per-segment basis. The values range from 0 to 1, where 1 is a rectangle.
If the only input into
the tool is a segmented image, the default attributes are COLOR, COUNT,
COMPACTNESS, and RECTANGULARITY. If an Additional Input Raster is also included
as an input along with a segmented image, then MEAN and STD are available as
options.
Create Accuracy Assessment Points
How to use Create Accuracy
Assessment Points Tool in Arc Toolbox??
Create Accuracy Assessment Points
Path to access the tool
:
Create
Accuracy Assessment Points Tool, Segmentation
and Classification Toolset, Spatial Analyst Tools Toolbox
Create Accuracy Assessment Points
Creates randomly sampled
points for post-classification accuracy assessment.
A common practice is to
randomly select hundreds of points and label their classification types by
referencing reliable sources, such as field work or human interpretation of
high-resolution imagery. The reference points are then compared with the
classification results at the same locations.
1. Input Raster Or Feature Class
The input classification
image or other thematic GIS reference data. The input can be a raster or
feature class.
Typical data is a
classification image (single band, integer data type), or the training polygon
output from an ArcMap image classification toolbar.
If using polygons as
input, only use those that are not used as training samples. They can also be
GIS land-cover data in shapefile or feature class format.
2. Output Accuracy Assessment Points
The output point
shapefile or feature class that contains the random points to be used for
accuracy assessment.
3. Target Field (optional)
Specifies whether your input data is a classified image or ground truth data.
- CLASSIFIED—The input is a classified image. This is the default.
- GROUND_TRUTH—The input is reference data.
4. Number of Random Points (optional)
The total number of
random points that will be generated.
The actual number may
exceed but never fall below this number, depending on sampling strategy and
number of classes. The default number of randomly generated points is 500.
5. Sampling Strategy (optional)
Specify a sampling scheme to use.
- STRATIFIED_RANDOM—Create points that are randomly distributed within each class, where each class has a number of points proportional to its relative area. This is the default
- EQUALIZED_STRATIFIED_RANDOM—Create points that are randomly distributed within each class, where each class has the same number of points.
- RANDOM—Create points that are randomly distributed throughout the image.

Comments
Post a Comment