Average Nearest Neighbor, High/Low Clustering Tools
Average Nearest Neighbor
How to use Average Nearest Neighbor Tool in ArcToolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??
 |
| Average Nearest Neighbor Tool |
Path to access the tool
:
Average Nearest Neighbor Tool, Analyzing Patterns Toolset, Spatial Statistics Tools Toolbox
Average Nearest Neighbor
Calculates a nearest
neighbor index based on the average distance from each feature to its nearest
neighboring feature.
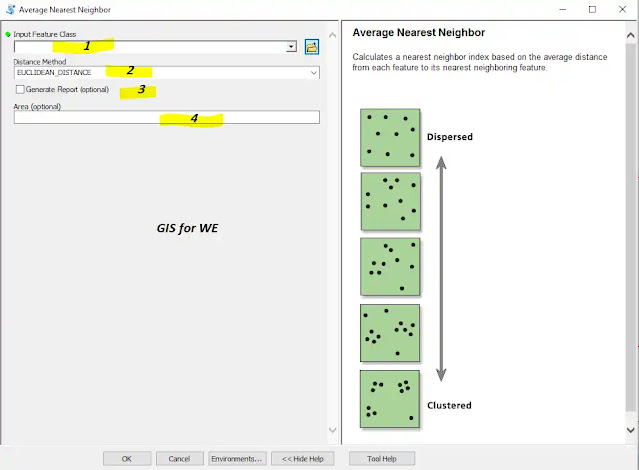
1. Input Feature Class
The feature class,
typically a point feature class, for which the average nearest neighbor
distance will be calculated.
2. Distance Method
Specifies how distances
are calculated from each feature to neighboring features.
·
EUCLIDEAN_DISTANCE—The straight-line distance between two points
(as the crow flies)
·
MANHATTAN_DISTANCE—The distance between two points measured along
axes at right angles (city block); calculated by summing the (absolute)
difference between the x- and y-coordinates
3. Generate Report (optional)
Specifies whether the
tool will create a graphical summary of results.
·
Checked—A graphical summary will be created as an HTML file.
·
Unchecked—No graphical summary will be created. This is the
default.
4. Area (optional)
A numeric value representing the study area
size. The default value is the area of the minimum enclosing rectangle that
would encompass all features (or all selected features). Units should match
those for the Output Coordinate System.
High/Low Clustering (Getis-Ord General G)Tool
How to use High/Low Clustering (Getis-Ord General G) Tool in ArcToolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??
 |
| High/Low Clustering (Getis-Ord General G) Tool |
Path to access the tool
:
High/Low Clustering (Getis-Ord General G) Tool, Analyzing Patterns Toolset, Spatial Statistics Tools Toolbox
High/Low Clustering (Getis-Ord General G)
Measures the degree of
clustering for either high values or low values using the Getis-Ord General G
statistic.
You can access the
results of this tool (including the optional report file) from the Results
window. If you disable background processing, results will also be written to
the Progress dialog box.
1. Input Feature Class
The feature class for
which the General G statistic will be calculated.
2. Input Field
The numeric field to be
evaluated.
3. Generate Report (optional)
Specifies whether the
tool will create a graphical summary of results.
·
Checked—A graphical summary will be created as an HTML file.
·
Unchecked—No graphical summary will be created. This is the
default.
4. Conceptualization of Spatial Relationships
Specifies how spatial
relationships among features are defined.
·
INVERSE_DISTANCE—Nearby neighboring features have a larger
influence on the computations for a target feature than features that are far
away.
·
INVERSE_DISTANCE_SQUARED—Same asINVERSE_DISTANCE except that the
slope is sharper, so influence drops off more quickly, and only a target
feature's closest neighbors will exert substantial influence on computations
for that feature.
·
FIXED_DISTANCE_BAND—Each feature is analyzed within the context of
neighboring features. Neighboring features inside the specified critical
distance (Distance Band or Threshold Distance) receive a weight of one and
exert influence on computations for the target feature. Neighboring features
outside the critical distance receive a weight of zero and have no influence on
a target feature's computations.
·
ZONE_OF_INDIFFERENCE—Features within the specified critical
distance (Distance Band or Threshold Distance) of a target feature receive a
weight of one and influence computations for that feature. Once the critical
distance is exceeded, weights (and the influence a neighboring feature has on
target feature computations) diminish with distance.
·
CONTIGUITY_EDGES_ONLY—Only neighboring polygon features that share
a boundary or overlap will influence computations for the target polygon
feature.
·
CONTIGUITY_EDGES_CORNERS—Polygon features that share a boundary,
share a node, or overlap will influence computations for the target polygon
feature.
·
GET_SPATIAL_WEIGHTS_FROM_FILE—Spatial relationships are defined by
a specified spatial weights file. The path to the spatial weights file is
specified by the Weights Matrix File parameter.
5. Distance Method
Specifies how distances
are calculated from each feature to neighboring features.
·
EUCLIDEAN_DISTANCE—The straight-line distance between two points
(as the crow flies)
·
MANHATTAN_DISTANCE—The distance between two points measured along
axes at right angles (city block); calculated by summing the (absolute)
difference between the x- and y-coordinates
6. Standardization
Row standardization is
recommended whenever the distribution of your features is potentially biased
due to sampling design or an imposed aggregation scheme.
·
NONE—No standardization of spatial weights is applied.
·
ROW—Spatial weights are standardized; each weight is divided by
its row sum (the sum of the weights of all neighboring features).
7. Distance Band or Threshold Distance (optional)
- Specifies a cutoff distance for Inverse Distance and Fixed Distance options. Features outside the specified cutoff for a target feature are ignored in analyses for that feature. However, for Zone of Indifference, the influence of features outside the given distance is reduced with distance, while those inside the distance threshold are equally considered. The distance value entered should match that of the output coordinate system.
- For the inverse distance conceptualizations of spatial
relationships, a value of 0 indicates that no threshold distance is applied;
when this parameter is left blank, a default threshold value is computed and
applied. This default value is the Euclidean distance that ensures every
feature has at least one neighbor.
- This parameter has no effect when polygon contiguity (CONTIGUITY_EDGES_ONLY or CONTIGUITY_EDGES_CORNERS) or GET_SPATIAL_WEIGHTS_FROM_FILE spatial conceptualizations are selected.
8. Weights Matrix File (optional)
The path to a file containing weights that define spatial, and potentially temporal, relationships among features.

Comments
Post a Comment