TIN Polygon Tag and Triangle, TIN to Raster
TIN Polygon Tag
How to use TIN Polygon Tag Tool in Arc Toolbox ArcMap ArcGIS ??
 |
| TIN Polygon |
TIN Polygon Tag Tool, From TIN Toolset, Conversion Toolset, 3D Analyst Toolbox
TIN Polygon Tag
Creates polygon features
using tag values in a triangulated irregular network (TIN) dataset.
1. Input TIN
The TIN dataset to process.
2. Output Feature Class
The feature class that will be produced by this tool.
3. Tag Value Field (optional)
The name of the field
storing the tag attribute in the output feature class. The default field name
is Tag_Value.
TIN to Raster
How to use TIN to Raster Tool in Arc Toolbox ArcMap ArcGIS ??
 |
| TIN to Raster |
TIN to Raster Tool, From TIN Toolset, Conversion Toolset, 3D Analyst Toolbox
TIN to Raster
Interpolates a raster using z-values from the input TIN.
1. Input TIN
The TIN dataset to
process.
2. Output Raster
The location and name of
the output raster. When storing a raster dataset in a geodatabase or in a
folder such as an Esri Grid, no file extension should be added to the name of
the raster dataset. A file extension can be provided to define the raster's
format when storing it in a folder, such as .tif to generate a GeoTIFF or .img
to generate an ERDAS IMAGINE format file.
If the raster is stored
as a TIFF file or in a geodatabase, its raster compression type and quality can
be specified using geoprocessing environment settings.
3. Output Data Type (optional)
Specifies the type of
numeric values stored in the output raster.
·
FLOAT—Output raster will use 32-bit floating point, which supports
values ranging from -3.402823466e+38 to 3.402823466e+38. This is the default.
·
INT—Output raster will use an appropriate integer bit depth. This
option will round z-values to the nearest whole number and write an integer to
each raster cell value.
4. Method (optional)
The interpolation method
used to create the raster.
·
LINEAR—Calculates cell values by applying linear interpolation to
the TIN triangles. This is the default.
·
NATURAL_NEIGHBORS—Calculates cell values by using natural
neighbors interpolation of TIN triangles
5. Sampling Distance (optional)
The sampling method and distance used to define
the cell size of the output raster.
6. Z Factor (optional)
The factor by which z-values will be multiplied.
This is typically used to convert Z linear units to match XY linear units. The
default is 1, which leaves elevation values unchanged. This parameter is
disabled if the spatial reference of the input surface has a Z datum with a
specified linear unit.
TIN Triangle
How to use TIN Triangle Tool in Arc Toolbox ArcMap ArcGIS ??
 |
| TIN Triangle |
TIN Triangle Tool, From TIN Toolset, Conversion Toolset, 3D Analyst
Toolbox
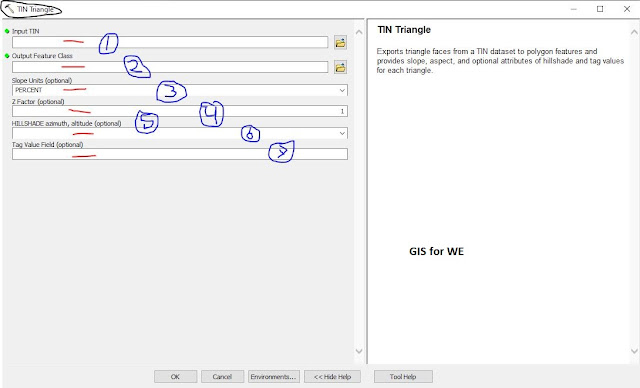
TIN Triangle
Exports triangle faces
from a TIN dataset to polygon features and provides slope, aspect, and optional
attributes of hillshade and tag values for each triangle.
1. Input TIN
The TIN dataset to
process.
2. Output Feature Class
The feature class that
will be produced by this tool.
3. Slope Units (optional)
The units of measure to
be used in calculating slope.
·
PERCENT—Slope is expressed as a percentage value. This is the
default.
·
DEGREE—Slope is expressed as the angle of inclination from a
horizontal plane.
4. Z Factor (optional)
The factor by which z-values will be multiplied.
This is typically used to convert Z linear units to match XY linear units. The
default is 1, which leaves elevation values unchanged. This parameter is
disabled if the spatial reference of the input surface has a Z datum with a
specified linear unit.
5. HILLSHADE azimuth, altitude (optional)
Specifies the azimuth and altitude angles of the
light source when applying a hillshade effect for the feature layer output.
Azimuth can range from 0 to 360 degrees, whereas altitude can range from 0 to
90. An azimuth of 45 degrees and altitude of 30 degrees would be entered as
"HILLSHADE 45, 30".
6. Tag Value Field (optional)
The field name in the output feature that will
store the triangle tag value. This parameter is empty by default, which will
result in tag values not being written to the output.

Comments
Post a Comment