Nibble, Region Group, Shrink and Thin Tools
Nibble
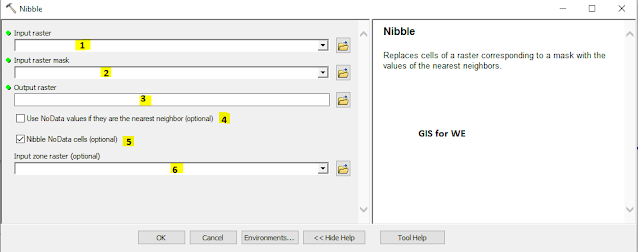
How to use Nibble Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
| Nibble Tool |
Path to access the tool
:
Nibble Tool, Generalization Toolset,
Spatial Analyst Tools Toolbox
Nibble
Replaces cells of a
raster corresponding to a mask with the values of the nearest neighbors.
1. Input raster
The input raster that
will be nibbled.
The input raster can be
either integer or floating-point type.
2. Input raster mask
The raster used as the
mask.
Cells that are NoData in
the mask raster identify the cells in the Input raster that will be nibbled, or
replaced, by the value of the closest nearest neighbour.
The mask raster can be
either integer or floating-point type.
3. Output raster
The output nibbled
raster.
The identified input
cells will be replaced with the values of their nearest neighbors.
If the Input raster is
integer, the output raster will be integer. If it is floating point, the output
will be floating point.
4. Use NoData values if they are the nearest neighbor (optional)
Defines whether or not NoData cells in the input raster are allowed to nibble into the area defined by the mask raster.
- Checked—Specifies that the nearest neighbor value will be used whether it is NoData or another data value in the input raster. NoData values in the input raster are free to nibble into areas defined in the mask if they are the nearest neighbor. This is the default.
- Unchecked—Specifies that only data values are free to nibble into areas defined in the mask raster. NoData values in the input raster are not allowed to nibble into areas defined in the mask raster even if they are the nearest neighbor.
5. Nibble NoData cells (optional)
Defines if NoData cells in the input raster that are within the mask will remain NoData in the output raster.
- Unchecked—Specifies that NoData cells in the input raster and within the mask will remain NoData in the output. This is the default.
- Checked—Specifies that NoData cells in the input raster and within the mask can be nibbled into valid output cell values.
6. Input zone raster (optional)
The input zone raster.
For each zone, input cells that are within the mask will be replaced only by
the nearest cell values within that same zone.
A zone is all the cells
in a raster that have the same value, whether or not they are contiguous. The
input zone layer defines the shape, values, and locations of the zones. The
zone raster can be either integer or floating point type.
Region Group
How to use Region Group Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
| Region Group |
Path to access the tool
:
Region
Group Tool, Generalization Toolset,
Spatial Analyst Tools Toolbox
Region Group
For each cell in the
output, the identity of the connected region to which that cell belongs is
recorded. A unique number is assigned to each region.
1. Input raster
The input raster whose
unique connected regions will be identified.
It must be of integer
type.
2. Output raster
The output region group
raster.
The output is always of
integer type.
3. Number of neighbors to use (optional)
The number of neighboring cells to use in evaluating connectivity between cells.
- FOUR—Defines connectivity between cells of the same value only if the cells are directly to the left, right, above, or below each of the four nearest neighbors. If two cells with the same value are diagonal from one another, they are not considered connected. This is the default.
- EIGHT—Defines connectivity between cells of the same value if they are within the immediate eight-cell neighborhood (eight nearest neighbors) of each other. This includes to the right, left, above, or diagonal to each other.
4. Zone grouping method (optional)
Defines which cell values should be considered when testing for connectivity.
- WITHIN—Tests connectivity between input values that are the same within the same zone.The only cells that can be grouped are cells from the same zone (value) that meet the spatial requirements of connectivity specified by the Number of neighbours parameter (four-way or eight-way). This is the default.
- CROSS—Tests connectivity by the spatial requirements specified by the Number of neighbors to use parameter between cells with any values, except for the value identified to be excluded by the Excluded value parameter.When CROSS is used, a value for the Excluded value parameter must be input.
5. Add link field to output (optional)
Specifies whether a link field is added to the table of the output.
- Checked—A LINK item will be added to the table of the output raster. This item stores the original values for each newly created zone, from disconnected regions, from the input raster before they are regrouped. This is the default.
- Unchecked—The attribute table for the output raster will only contain the Value and Count items.
6. Excluded value (optional)
Identifies a value such
that if a cell location contains the value, no spatial connectivity will be
evaluated regardless how the number of neighbors is specified (FOUR or EIGHT).
Cells with the excluded
value will be treated as NoData and are eliminated from calculations. Cell
locations that contain the excluded value will receive 0 on the output raster.
The excluded value is
similar to the concept of a background value, or setting a mask in the
environment for a single run of the tool. A value must be specified for this
parameter if the CROSS keyword is specified.
Shrink
How to use Shrink Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
| Shrink Tool |
Path to access the tool
:
Shrink Tool, Generalization Toolset,
Spatial Analyst Tools Toolbox
Shrink
Shrinks the selected
zones by a specified number of cells by replacing them with the value of the
cell that is most frequent in its neighborhood.
1. Input raster
The input raster for
which the identified zones are to be shrunk.
It must be of integer
type.
2. Output raster
The output generalized
raster.
The specified zones of
the input raster will be shrunk by the specified number of cells.
The output is always of
integer type.
3. Number of cells
The number of cells by
which to shrink each specified zone.
The value must be an
integer greater than 0.
4. Zone values
The list of zone values
to shrink.
The zone values must be
integers. They can be in any order.
Thin
How to use Thin Tool in Arc Toolbox??
 |
| Thin |
Path to access the tool
:
Thin Tool, Generalization Toolset,
Spatial Analyst Tools Toolbox
Thin
Thins rasterized linear features
by reducing the number of cells representing the width of the features.
1. Input raster
The input raster to be
thinned.
It must be of integer type.
2. Output raster
The output thinned
raster.
The output is always of
integer type.
3. Background value (optional)
Specifies the cell value that will identify the background cells. The linear features are formed from the foreground cells.
- ZERO—The background is composed of cells of 0 or less, or NoData. All cells whose value is greater than 0 are the foreground.
- NODATA— The background is composed of NoData cells. All cells with valid values belong to the foreground.
4. Filter input first (optional)
Specifies whether a filter will be applied as the first phase of thinning.
- Unchecked—No filter will be applied. This is the default.
- Checked—The raster will be filtered to smooth the boundaries between foreground and background cells. This option will eliminate minor irregularities from the output raster.
5. Shape for corners (optional)
Specifies whether round
or sharp turns will be made at turns or junctions.
It is also used during the vector conversion process to spline curves or create sharp intersections and corners.
- ROUND— Attempts to smooth corners and junctions. This is best for vectorizing natural features, such as contours or streams.
- SHARP— Attempts to preserve rectangular corners and junctions. This is best for vectorizing man-made features such as streets.
6. Maximum thickness of input linear features (optional) (اختياري)
The maximum thickness,
in map units, of linear features in the input raster.
The default thickness is ten times the cell size.

Comments
Post a Comment