Locate Regions
How to use Locate Regions Tool in Arc Toolbox??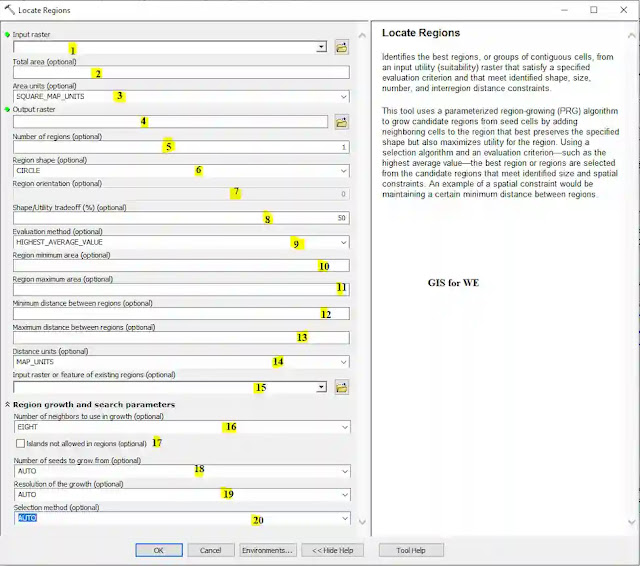
Locate Regions Tool

Path to access the tool
:
Locate
Regions Tool, Overlay Toolset, Spatial
Analyst Tools Toolbox
Locate Regions
Identifies the best
regions, or groups of contiguous cells, from an input utility (suitability)
raster that satisfy a specified evaluation criterion and that meet identified
shape, size, number, and interregion distance constraints.
This tool uses a
parameterized region-growing (PRG) algorithm to grow candidate regions from
seed cells by adding neighboring cells to the region that best preserves the
specified shape but also maximizes utility for the region. Using a selection
algorithm and an evaluation criterion—such as the highest average value—the
best region or regions are selected from the candidate regions that meet
identified size and spatial constraints. An example of a spatial constraint would
be maintaining a certain minimum distance between regions.
1. Input raster
The input utility raster
from which the regions will be derived.
The higher the value in
the input raster, the greater the utility.
The raster can be of
either integer or floating-point type.
2. Total area (optional)
The total amount of area
for all regions.
The default is 10
percent of the input cells within the processing extent.
3. Area units (optional)
Defines the area units
used for the Total area, Region minimum area, and Region maximum area parameters.
The available options and their corresponding units are the following:
- SQUARE_MAP_UNITS—For the square of the linear units of the output spatial reference
- SQUARE_MILES—For miles
- SQUARE_KILOMETERS—For kilometers
- HECTARES—For hectares
- ACRES—For acres
- SQUARE_METERS—For meters
- SQUARE_YARDS—For yards
- SQUARE_FEET—For feet
The default is based on
the input raster dataset. If the input raster is in feet, yards, miles, or any
other imperial unit, SQUARE_MILES will be used. If the input raster is in
meters, kilometers, or any other metric unit, SQUARE_KILOMETERS will be used.
4. Output raster
The output regions
raster.
Each region is uniquely
numbered with values greater than zero. Cells that do not belong to any regions
will be assigned zero. The output is always an integer raster.
Additional fields are calculated for each region storing statistics of the selected regions. These fields are the following:
- AVERAGE—The average utility value of the region.
- TOTAL—The total sum of the utility values within the region.
- MEDIAN—The median utility value of the region.
- HIGHEST—The highest individual cell value contained within the region.
- LOWEST—The lowest individual cell value contained within the region.
- COREAREA—The core area. Any cell farther than one cell from the region's edge is considered to be part of the core.
- CORESUM—The cumulative sum of the utility values for the core area.
- EDGE—The amount of edge using the P1 ratio, which is the ratio of the perimeter of the shape to the perimeter of a circle of the same area. The P1 ratio for a circle is 1.
5. Number of regions (optional)
Determines how many
regions the Total area will be distributed across.
The maximum number of
regions that can be specified is 30. The default is 1.
6. Region shape (optional)
Defines the shape
characteristics for the output regions.
The regions start out
from seed cell locations and grow outward with preference given to the cells
that maintain the desired shape.
The available shape options are the following:
- CIRCLE—Cells that maintain circular regions will receive a greater weight. This is the default.
- ELLIPSE—Cells that maintain elliptical-shaped regions will receive a greater weight.
- TRIANGLE—Cells that maintain equilateral triangular-shaped regions will receive a greater weight.
- SQUARE—Cells that maintain square-shaped regions will receive a greater weight.
- PENTAGON—Cells that maintain pentagon-shaped regions will receive a greater weight.
- HEXAGON—Cells that maintain hexagon-shaped regions will receive a greater weight.
- OCTAGON—Cells that maintain octagon-shaped regions will receive a greater weight.
7. Region orientation (optional)
Defines the orientation
of the defined shape. Regions are grown out from the seed locations with
preference given to the cells that maintain the desired orientation of the
region shapes.
The orientation values
are in compass degrees ranging from 0 to 360, increasing clockwise starting
from north. The default is 0.
The default of 0 orients
the shapes in the following manner: Circle—no effect; Ellipse—the minor axis is
orientated north-south; Triangle and Pentagon—one point is straight up; Square,
Hexagon, and Octagon—one flat side is oriented east-west.
If the Region shape is
set to CIRCLE, the Region orientation parameter is unavailable.
8. Shape/Utility tradeoff (%) (optional)
Identifies the weight
for the cells when growing the candidate regions in the parameterized
region-growing algorithm. The weighting is a tradeoff between a cell's
contribution for maintaining the region shape relative to the utility
contribution of the cell's attribute value.
Higher values indicates
maintaining the shape of the region is more important than selecting higher
utility values. The acceptable percent values are 0 to 100, inclusively. The
default is 50.
This parameter is used
to identify the feasible candidate regions. The candidate regions that will be
selected by the algorithm are controlled by the Evaluation method parameter.
9. Evaluation method (optional)
The evaluation criteria
to be used for determining which of the candidate regions identified in the parameterized
region-growing algorithm are most preferred. The preference can be specified
based on a particular statistic of the utility values, or spatial arrangement
of the cells within the regions.
The available options are the following:
- HIGHEST_AVERAGE_VALUE—Selects regions based on the highest average value. This is the default.
- HIGHEST_SUM—Selects regions based on the highest sum.
- HIGHEST_MEDIAN_VALUE—Selects regions based on the highest median value.
- HIGHEST_VALUE—Selects regions based on the highest individual cell value contained within the region. This option ensures the best individual cells are selected.
- LOWEST_VALUE—Selects regions based on the highest lowest individual cell value contained within the region. This option ensures the selected regions contain cells with really low utility.
- GREATEST_CORE_AREA—Selects regions based on the greatest core area.Any cell that is farther than one cell from the edge of a region is considered to be part of the core. The edge distance can be controlled by the analysis cell size. Setting a smaller cell size can increase the core area.
- HIGHEST_CORE_SUM—Selects regions based on the highest cumulative sum of the utility values for the core area. The edge distance can be controlled by the analysis cell size.
- GREATEST_EDGE—Selects regions based on the greatest amount of edge using the P1 ratio, which is the ratio of the perimeter of the shape to the perimeter of a circle of the same area. The P1 ratio for a circle is 1.
10. Region minimum area (optional)
Define the minimum area
allowed for each region.
The units specified by
the Area units parameter will be used.
11. Region maximum area (optional)
Define the maximum area
allowed for each region.
The units specified by
the Area units parameter will be used.
12. Minimum distance between regions (optional)
Define the minimum
distance allowed between regions. No two regions can be within this distance.
This parameter
influences the parameterized region-growing (PRG) algorithm. If a cell has the
potential of being added to a candidate region, but it is within this distance
from any individual region in the dataset specified by the Input raster or
feature of existing regions parameter, it will not be considered for the
candidate region. The minimum distance setting is not applied to excluded
locations (NoData cells).
The units specified by
the Distance units parameter will be used.
13. Maximum distance between regions (optional)
Define the maximum
distance allowed between regions. No region can be farther apart than this
distance from at least one other region.
When sequentially
selecting regions, if the next best region is farther than this distance from
any of the already selected regions, it will not be considered at this time,
but it may be selected later when more regions are selected.
The maximum distance is
applied to the dataset specified in the Input raster or feature of existing
regions parameter, in that at least one of the selected regions must be within
the maximum distance from existing regions. The maximum distance setting is not
applied to excluded areas (NoData cells) and has no effect on the PRG
algorithm.
The units specified by
the Distance units parameter will be used.
14. Distance units (optional)
Defines the distance
units that will be used for the Minimum distance between regions and Maximum
distance between regions parameters.
The available options and their corresponding units are the following:
- MAP_UNITS—For the linear units of the output spatial reference
- MILES—For miles
- KILOMETERS—For kilometers
- METERS—For meters
- YARDS—For yards
- FEET—For feet
The default is based on
the input raster dataset. If the input raster is in feet, yards, miles, or any
other imperial unit, MILES will be used. If the input raster is in meters,
kilometers, or any other metric unit, KILOMETERS will be used.
15. Input raster or feature of existing regions (optional)
A dataset identifying
where regions already exist.
The input can be a
raster or feature dataset. If the input is a raster, any location in the raster
with a valid value is considered already allocated. All other locations are set
to NoData.
In the parameterized
region-growing algorithm, no region will grow from any location identified as
an existing region. Existing regions will be used in the growth and evaluation
of the Minimum distance between regions and Maximum distance between regions
parameters as described in the corresponding parameter descriptions above.
16. Number of neighbors to use in growth (optional)
Defines which
neighboring cells to use in the growth of the regions.
The available options are the following:
- FOUR—Only the four direct (orthogonal) neighbors of the region cells will be considered in the region growth.
- EIGHT—The eight nearest neighbors (orthogonal and diagonal) will be considered in the region growth. This is the default.
17. Islands not allowed in regions (optional)
Defines whether or not islands will be allowed within the potential regions.
- Checked—The parameterized region-growing algorithm ensures there will be no islands within a region. This is the default.
- Unchecked—Islands will be allowed.
18. Number of seeds to grow from (optional)
Defines the number of
seeds from which to grow the potential regions.
The available options are the following:
- AUTO—The number of seeds will be based on the number of cells in the input raster. When the input raster has 100,000 cells or fewer, the default is Maximum. When the input raster has more than 100,000 cells, the default is Small. This is the default.
- SMALL—The number of seeds will be equal to 10 percent of the number of cells in the input raster, after NoData cells are excluded, but not to exceed 1,600 seeds.
- MEDIUM—The number of seeds will be equal to 20 percent of the number of cells in the input raster, after NoData cells are excluded, but not to exceed 2,500 seeds.
- LARGE—The number of seeds will be equal to 30 percent of the number of cells in the input raster, after NoData cells are excluded, but not to exceed 3,600 seeds.
- MAXIMUM—The region growth will occur at each available cell within the input raster. Available cells are all cells that are not NoData and not identified as an existing region.
19. Resolution of the growth (optional)
Sets the resolution at
which region growth occurs.
The input raster will be
resampled to the resolution determined by the number of cells identified by
this parameter (see below). For example, for LOW, the input raster is resampled
to 147,356 cells. The parameterized region-growing algorithm grows on the
resampled intermediate raster. Once the regions are selected from the resampled
intermediate raster, the selected regions will be resampled to the Environment
cell size.
An adjustment to the
target resolutions identified below may be implemented if the number of cells
in the desired average region size is too small or too large. This adjustment
makes sure there will be enough cells in each desired region or that
unnecessary processing will not occur. As a result, the total cells for the
intermediate resampled raster for each of the specified resolutions below can
be lower or higher than the target number of cells.
If the input has less
than 147,356 cells or MAXIMUM is selected, no resampling will occur and the
region growth will process on all cells in the input raster. If the input
raster has less than 147,356 cells, the LOW, MEDIUM, or HIGH options have no
effect.
The available options are the following:
- AUTO—The resolution will be based on the number of cells in the input raster. When the input raster has 500,000 cells or fewer, the default is Maximum. When the input raster has more than 500,000 cells, the default is Low. This is the default.
- LOW—The analysis will be performed on an intermediate raster containing 147,356 (384 x 384) cells distributed in the same x and y ratio as the input raster.
- MEDIUM—The analysis will be performed on an intermediate raster containing 262,144 (512 x 512) cells distributed in the same x and y ratio as the input raster.
- HIGH—The analysis will be performed on an intermediate raster containing 589,824 (768 x 768) cells distributed in the same x and y ratio as the input raster.
- MAXIMUM—The analysis will be performed on all cells in the input raster.
20. Selection method (optional)
Identifies how the
regions will be selected.
The available options are the following:
- AUTO—The selection method is based on the Number of regions parameter. If the Number of regions is eight or less, the Combinatorial selection method is used. If the Number of regions parameter is greater than eight, the Sequential selection method is used. This is the default.
- COMBINATORIAL—Selects the best regions based on the specified evaluation method, while honoring the spatial constraints, by testing all combinations of the desired number of regions within the candidate regions from the parameterized region-growing (PRG) algorithm.
- SEQUENTIAL—Sequentially selects the best regions based on the evaluation method and that meets the spatial constraints until the desired number of regions is reached.

Comments
Post a Comment