Generate Service Areas Tools
How to use Generate Service Areas Tool in Arc Toolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??
Path to access the tool
:
Generate
Service Areas Tool, Server Toolset, Network
Analyst Tools Toolbox
Generate Service Areas
Creates a service area
network analysis layer, sets the analysis properties, and solves the analysis.
This tool is ideal for setting up a service area geoprocessing service on the web.
A network service area is a region that encompasses all streets that can be
accessed within a given distance or travel time from one or more facilities.
Service areas are
commonly used to visualize and measure accessibility. For example, a 3-minute
drive-time polygon around a grocery store can determine which residents are
able to reach the store within 3 minutes and are thus more likely to shop
there.
The Generate Service
Areas and Make Service Area Layer tools are similar, but they are designed for
different purposes. Use Generate Service Areas if you are setting up a
geoprocessing service; it will simplify the setup process; otherwise, use Make
Service Area Layer. Also, use Make Service Area Layer if you need to generate
service area lines; Generate Service Areas doesn't provide the option to
generate lines.
To create a service-area
geoprocessing service using Generate Service Areas, you only need to set up one
tool, and you can publish the tool directly as a service. In contrast, you need
to create a model with the Make Service Area Layer, properly connect it to
various other tools, and publish the model to create a service-area
geoprocessing service. See Geoprocessing service example: Drive-time polygons
to learn how to set up a drive-time polygons service using tutorial data. One
other option to consider is the ArcGIS Online Generate Service Areas service.
The service runs like a geoprocessing tool in ArcMap, can be accessed from
other applications, and includes high-quality road data for much of the world.
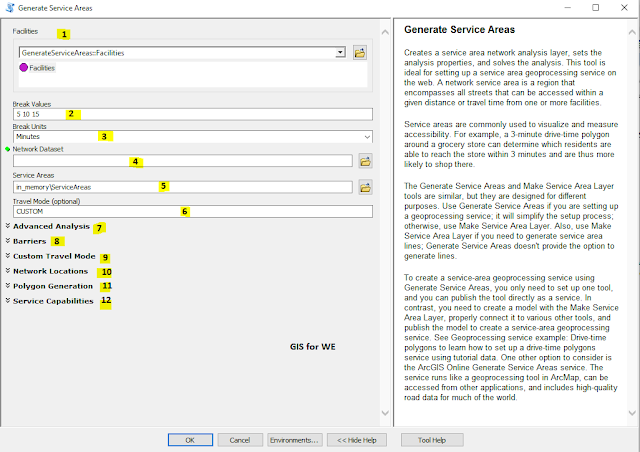
1. Facilities
The facilities around
which service areas are generated.
The facilities feature
set has three attributes:
ObjectID:
The system-managed ID
field.
Shape:
The geometry field
indicating the geographic location of the network analysis object.
Name:
The name of the
facility. If the name is empty, blank, or null, a name is automatically
generated at solve time.
2. Break Values
Specifies the size and
number of service area polygons to generate for each facility. The units are
determined by the Break Units value.
When the Generate
Service Areas tool runs, a noteworthy interaction occurs among the following
parameters: Break Values, Break Units, and either Time Attribute or Distance
Attribute. Together, Break Values and Break Units define how far or how long
the service area should extend around the facility or facilities. The Time
Attribute and Distance Attribute parameters each define one network cost
attribute. Only one of these two cost attributes is used, however, and the one
that the solver chooses to use corresponds with the Break Units value; that is,
when you specify a time-based Break Units value, such as seconds or minutes,
the tool solves using the cost attribute defined in the Time Attribute
parameter. When you specify a distance-based Break Units value, such as
kilometers or miles, it uses the cost attribute defined in the Distance
Attribute parameter.
Multiple polygon breaks
can be set to create concentric service areas per facility. For instance, to
find 2-, 3-,
and 5-mile service areas for each facility, enter 2 3 5,
separating the values with a space. Set Break Units to Miles and ensure that
you have chosen a distance-based network attribute for the Distance Attribute
parameter.
3. Break Units
The units for the Break Values parameter.
- Meters
- Kilometers
- Feet
- Yards
- Miles
- Nautical Miles
- Seconds
- Minutes
- Hours
- Days
The Generate Service
Areas tool chooses whether to use the network cost attribute specified in the
Time Attribute or Distance Attribute parameter depending on whether the units you
specify here are time or distance based.
The tool performs the
necessary units conversion when the Break Units value differs from the units of
the corresponding time or distance cost attribute.
4. Network Dataset
The network dataset on
which the analysis will be performed. Network datasets most often represent
street networks but may represent other kinds of transportation networks as
well. The network dataset needs at least one time-based and one distance-based
cost attribute.
5. Service Areas
The output workspace and
name of the output features. This workspace must already exist. The default
output workspace is in_memory.
6. Travel Mode (optional)
Choose the mode of
transportation for the analysis. Custom is always a choice. For other travel
mode names to appear, they must be present in the network dataset specified in
the Network Dataset parameter.
A travel mode is defined on a network dataset and provides override values for parameters that, together, model cars, trucks, pedestrians, or other modes of travel. By choosing a travel mode here, you don't need to provide values for the following parameters, which are overridden by values specified in the network dataset:
- UTurn Policy
- Time Attribute
- Time Attribute Units
- Distance Attribute
- Distance Attribute Units
- Use Hierarchy in Analysis
- Restrictions
- Attribute Parameter Values
- Polygon Simplification Tolerance
- CUSTOM—Define a travel mode that fits your specific needs. When Custom is chosen, the tool does not override the travel mode parameters listed above. This is the default value.
7. Advanced Analysis
8.
Barriers
9.
Custom Travel Mode
10.
Network Dataset
11.
Network Location
12.
Output
13.
Service Capabilities
All the seven additional categories are explained in detail, click here to access their explanation

Comments
Post a Comment