Areal Interpolation Layer to Polygons, Calculate Z-value, Create Geostatistical Layer, GA Layer to Contour and Grid and Points and Points, Get and Set Model Parameter Tools
Areal Interpolation Layer to Polygons
How to use Areal
Interpolation Layer to Polygons Tool in Arc Toolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??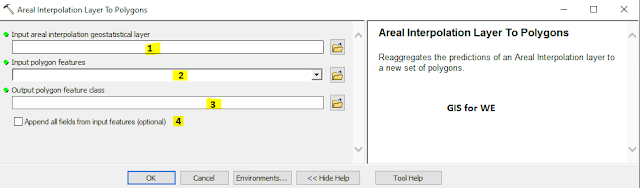
Areal Interpolation Layer to Polygons
Path to access the tool
:
Areal
Interpolation Layer to Polygons Tool, Working with Geostatistical Layers Toolset,
Geostatistical Analyst Tools Toolbox
Areal Interpolation Layer to
Polygons
Reaggregates the
predictions of an Areal Interpolation layer to a new set of polygons.
1. Input areal interpolation geostatistical layer
Input geostatistical
layer resulting from an Areal Interpolation model.
2. Input polygon features
The polygons where predictions
and standard errors will be aggregated.
3. Output polygon feature class
The output feature class
containing the aggregated predictions and standard errors for the new polygons.
4. Append all fields from input features (optional)
Determines whether all fields will be copied from the input features to the output feature class.
- Checked—All fields from the input features will be copied to the output feature class. This is the default.
- Unchecked—Only the feature ID value will be copied, and it will be named Source_ID on the output feature class.
Calculate Z-value
How to use Calculate
Z-value Tool in Arc Toolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??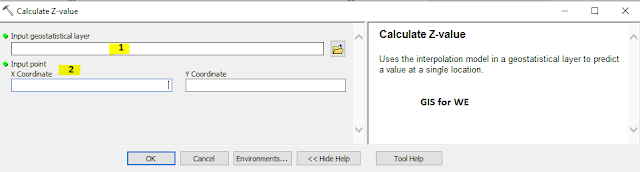
Calculate Z-value
Path to access the tool
:
Calculate
Z-value Tool, Working with Geostatistical Layers Toolset, Geostatistical
Analyst Tools Toolbox
Calculate Z-value
Uses the interpolation
model in a geostatistical layer to predict a value at a single location.
1. Input geostatistical layer
The geostatistical layer
to be analyzed.
2. Input point
The x,y coordinate of
the point for which the Z-value will be calculated.
Create Geostatistical Layer
How to use Create
Geostatistical Layer Tool in Arc Toolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??
Create Geostatistical Layer
Path to access the tool
:
Create
Geostatistical Layer Tool, Working with Geostatistical
Layers Toolset, Geostatistical Analyst Tools Toolbox
Create Geostatistical Layer
Creates a new
geostatistical layer. An existing geostatistical layer or geostatistical model
is required to populate the initial values for the new layer. The input to this
tool can be created using the Geostatistical Wizard.
1. Input geostatistical model source
The geostatistical model
source to be analyzed.
2. Input dataset(s)
The name of the input
datasets and field names used in the creation of the output layer.
When checked, the Always
reset input datasets when the geostatistical model source changes parameter
ensures that when a different geostatistical model source is specified, its
associated datasets are automatically inserted into the tool.
If unchecked and the
geostatistical model source is changed, the displayed input datasets remain
unchanged. This can lead to problems if the model is incompatible with the
dataset; for example, a model was created to predict temperature, and a new
dataset with rainfall data is specified.
3. Output geostatistical layer
The geostatistical layer
produced by the tool.
GA Layer to Contour
How to use GA Layer to
Contour Tool in Arc Toolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??
GA Layer to Contour
Path to access the tool
:
GA
Layer to Contour Tool, Working with Geostatistical
Layers Toolset, Geostatistical Analyst Tools Toolbox
GA Layer to Contour
Creates a feature class
of contours from a geostatistical layer.
The output feature class can be either
a line feature class of contour lines or a polygon feature class of filled
contours.
1. Input geostatistical layer
The geostatistical layer
to be analyzed.
2. Contour type
Type of contour to represent the geostatistical layer.
- CONTOUR— The contour or isoline representation of the geostatistical layer. Displays the lines in either draft or presentation quality.
- FILLED_CONTOUR—The polygon representation of the geostatistical layer. It assumes for the graphical display that the values between contour lines are the same for all locations within the polygon. Displays the lines in either draft or presentation quality.
- SAME_AS_LAYER—Use the current renderer of the input geostatistical layer. If the geostatistical layer is not rendered as either contour or filled contour, this option will created filled contours. Similarly, if the geostatistical layer is rendered as both contour and filled contour, this option will create filled contours.
3. Output feature class
The output feature class
will either be a polyline or a polygon, depending on the selected contour type.
4. Contour quality (optional)
Determines the smoothness of contour line representation.
- DRAFT— The default Draft quality presents a generalized version of isolines for faster display.
- PRESENTATION—The Presentation option ensures more detailed isolines for the output feature class.
5. Classification type (optional)
Specifies how the contour breaks will be calculated.
- GEOMETRIC_INTERVAL—Contour breaks are calculated based on geometric intervals.
- EQUAL_INTERVAL—Contour breaks are calculated based on equal intervals.
- QUANTILE—Contour breaks are calculated from quantiles of the input data.
- MANUAL—Specify your own break values.
6. Number of classes (optional)
Specify the number of
classes in the output feature class.
If Contour type is set
to output filled contour polygons, the number of polygons created will equal
the value specified in this parameter. If it is set to output contour
polylines, the number of polylines will be one less than the value specified in
this parameter (because N class intervals define N-1 contour break values).
This parameter does not
apply if the Classification type is set to Manual.
7. Class breaks (optional)
The list of break values if the Classification type is set to Manual.
- For contour output, these are the values of the contour lines.
- For filled contour, these are the upper limits of each class interval. Note that if the largest break value is less than the maximum of the geostatistical layer, the output feature class will not fill up the entire rectangular extent; all locations with predicted values above the largest break will not receive filled contours.
GA Layer to Grid
How to use GA Layer to Grid Tool in Arc Toolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??
GA Layer to Grid
Path to access the tool
:
GA
Layer to Grid Tool, Working with Geostatistical
Layers Toolset, Geostatistical Analyst Tools Toolbox
GA Layer to Grid
Exports a Geostatistical
layer to a raster.
1. Input geostatistical layer
The geostatistical layer
to be analyzed.
2. Output surface raster
The raster to be
created.
3. Output cell size (optional)
The cell size at which
the output raster will be created.
This value can be
explicitly set under Raster Analysis from the Environment Settings.
If not set, it is the
shorter of the width or the height of the extent of the input point features,
in the input spatial reference, divided by 250.
4. Number of points in the cell (horizontal) (optional)
The number of
predictions for each cell in the horizontal direction for block interpolation.
5. Number of points in the cell (vertical) (optional)
The number of
predictions for each cell in the vertical direction for block interpolation.
GA Layer to Points
How to use GA Layer to
Points Tool in Arc Toolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??
GA Layer to Points
Path to access the tool
:
GA
Layer to Points Tool, Working with Geostatistical
Layers Toolset, Geostatistical Analyst Tools Toolbox
GA Layer to Points
Exports a geostatistical
layer to points.
The tool can also be used to predict values at unmeasured
locations or to validate predictions made at measured locations.
1. Input geostatistical layer
The geostatistical layer
to be analyzed.
2. Input point observation locations
Point locations where
predictions or validations will be performed.
3. Field to validate on (optional)
If this field is left
blank, predictions are made at the location points. If a field is selected,
predictions are made at the location points, compared to their Z_value_field
values, and a validation analysis is performed.
4. Output statistics at point locations
The output feature class
containing either the predictions or the predictions and the validation
results.
The fields in this feature class can include the following fields (where applicable):
- Source_ID (Source ID)—The object ID of the source feature in the Input point observation locations.
- The feature or object identifier of the input dataset that was used.
- Yes—There are no problems making a prediction at this point.
- Not enough neighbors—There are not enough neighbors to make a prediction.
- Weight parameter is too small—The weight parameter is too small.
- Overfilling—Overflow of floating-point calculations.
- Problem with data transformation—The value to be transformed is outside of the supported range for the selected transformation (only in kriging).
- Predicted (Predicted)—The prediction value at this location.
- Error (Error)—The predicted value minus the value in the validation field.
- StdError (Standard Error)—The kriging standard error.
- Stdd_Error (Standardized Error)—The standardized prediction errors. Ideally, the standardized prediction errors are distributed normally.
- NormValue (Normal Value)—The normal distribution value (x-axis) that corresponds to the standardized prediction errors (y-axis) in the normal QQplot.
5. Append all fields from input features (optional)
Determines whether all fields will be copied from the input features to the output feature class.
- Checked—All fields from the input features will be copied to the output feature class. This is the default.
- Unchecked—Only the feature ID value will be copied, and it will be named Source_ID on the output feature class.
Get Model Parameter
How to use Get Model
Parameter Tool in Arc Toolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??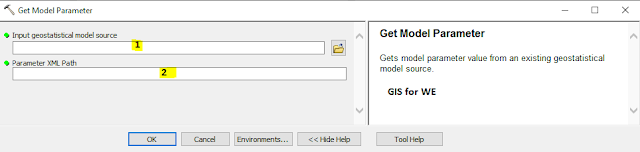
Get Model Parameter
Path to access the tool
:
Get
Model Parameter Tool, Working with Geostatistical
Layers Toolset, Geostatistical Analyst Tools Toolbox
Get Model Parameter
Gets model parameter
value from an existing geostatistical model source.
1. Input geostatistical model source
The geostatistical model
source to be analyzed.
2. Parameter XML Path
XML path to the required
model parameter.
Set Model Parameter
How to use Set Model
Parameter Tool in Arc Toolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??
Set Model Parameter
Path to access the tool
:
Set
Model Parameter Tool, Working with Geostatistical
Layers Toolset,
Geostatistical Analyst Tools Toolbox
Set Model Parameter
Sets parameter values in
an existing geostatistical model source.
1. Input geostatistical model source
The geostatistical model
source to be analyzed.
2. Parameter XML Path
XML path to the required
model parameter.
3. Parameter value
Value for the parameter
defined by the XML path.
4. Output model
Geostatistical model created with the parameter value defined in the XML path.

Comments
Post a Comment