Select Layer by Attribute and by Location, Save To Layer File Tools
Save To Layer File
How to Save To Layer File Tool in ArcToolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??
Save To Layer File
Path to access the tool
:
Save
To Layer File Tool, Layers and Table Views Toolset, Data Management Tools Toolbox
Save To Layer File
Creates an output layer
file (.lyr) from a map layer. The layer file stores many properties of the
input layer such as symbology, labeling,
and custom pop-ups.
1. Input Layer
The map layer to be
saved to disk as a layer file.
2. Output Layer
The output layer file
(.lyr) to be created.
3. Store Relative Path (optional)
Determines if the output layer file will store a relative path to the source data stored on disk, or an absolute path.
- Unchecked—The output layer file will store an absolute path to the source data stored on disk. This is the default.
- Checked—The output layer file will store a relative path to the source data stored on disk. If the output layer file is moved, its source path will update to where the source data should be in relation to the new path.
4. Layer Version (optional)
The version of the output layer file.
- CURRENT—The current version. This is the default.
- 10.4—10.4
- 10.3—10.3
- 10.2—10.2
- 10.1—10.1
- 10—10
- 9.3—9.3
- 9.2—9.2
- 9.1—9.1
- 9.0—9.0
- 8.3—8.3
Select Layer by Attribute
How to Select Layer by
Attribute Tool in ArcToolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??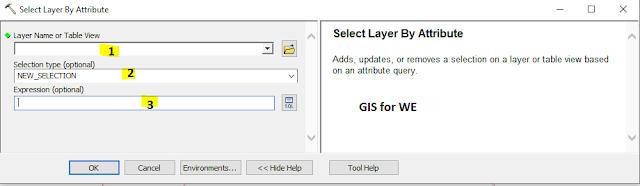
Select Layer by Attribute
Path to access the tool
:
Select
Layer by Attribute Tool, Layers and Table Views Toolset, Data Management Tools Toolbox
Select Layer by Attribute
Adds, updates, or removes a selection on a layer or table view based on an attribute query.
1.
Layer Name or Table View
The feature layer or
table view to which the selection will be applied.
The input can be a layer or table view in the ArcMap table of contents, or a layer or table view created in ArcCatalog or in scripts using the Make Feature Layer or Make Table View tools.
2.
Selection type (optional)
Determines how the selection will be applied and what to do if a selection already exists.
- NEW_SELECTION—The resulting selection replaces any existing selection. This is the default.
- ADD_TO_SELECTION—The resulting selection is added to an existing selection if one exists. If no selection exists, this is the same as the NEW_SELECTION option.
- REMOVE_FROM_SELECTION—The resulting selection is removed from an existing selection. If no selection exists, this option has no effect.
- SUBSET_SELECTION—The resulting selection is combined with the existing selection. Only records that are common to both remain selected.
- SWITCH_SELECTION—Switches the selection. All records that were selected are removed from the selection; all records that were not selected are added to the selection. The Expression is ignored when this option is specified.
- CLEAR_SELECTION—Clears or removes any selection. The Expression is ignored when this option is specified.
3. Expression (optional)
An SQL expression used
to select a subset of records.
Select Layer by Location
How to Select Layer by
Location Tool in ArcToolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??
Select Layer by Location
Path to access the tool
:
Select
Layer by Location Tool, Layers and Table Views Toolset, Data Management Tools Toolbox
Select Layer by Location
Selects features in a
layer based on a spatial relationship to features in another layer.
Each feature in the
Input Feature Layer is evaluated against the features in the Selecting Features
layer or feature class; if the specified Relationship is met, the input feature
is selected.
1. Input Feature Layer
The layer containing the
features that will be evaluated against the Selecting Features. The selection
will be applied to this layer. The input cannot be the path to a feature class
on disk.
2. Relationship (optional)
The spatial relationship to be evaluated.
- INTERSECT—The features in the input layer will be selected if they intersect a selecting feature. This is the default.
- INTERSECT_3D —The features in the input layer will be selected if they intersect a selecting feature in three-dimensional space (x, y, and z).
- WITHIN_A_DISTANCE—The features in the input layer will be selected if they are within a specified distance of a selecting feature. Specify a distance in the Search Distance parameter.
- WITHIN_A_DISTANCE_3D—The features in the input layer will be selected if they are within a specified distance of a selecting feature in three-dimensional space. Specify a distance in the Search Distance parameter.
- WITHIN_A_DISTANCE_GEODESIC—The features in the input layer will be selected if they are within a specified distance of a selecting feature. Distance between features will be calculated using a geodesic method which takes into account the curvature of the earth and correctly deals with data near and across the dateline and poles.
- CONTAINS—The features in the input layer will be selected if they contain a selecting feature.
- COMPLETELY_CONTAINS—The features in the input layer will be selected if they completely contain a selecting feature.
- CONTAINS_CLEMENTINI—This spatial relationship yields the same results as COMPLETELY_CONTAINS with the following exception: if the selecting feature is entirely on the boundary of the input feature (no part is properly inside or outside), the feature will not be selected. Clementini defines the boundary polygon as the line separating inside and outside, the boundary of a line is defined as its end points, and the boundary of a point is always empty.
- WITHIN—The features in the input layer will be selected if they are within a selecting feature.
- COMPLETELY_WITHIN—The features in the input layer will be selected if they are completely within or contained by a selecting feature.
- WITHIN_CLEMENTINI—The result will be identical to WITHIN with the exception that if the entirety of the feature in the input layer is on the boundary of the feature in the selecting layer, the feature will not be selected. Clementini defines the boundary polygon as the line separating inside and outside, the boundary of a line is defined as its end points, and the boundary of a point is always empty.
- ARE_IDENTICAL_TO—The features in the input layer will be selected if they are identical (in geometry) to a selecting feature.
- BOUNDARY_TOUCHES—The features in the input layer will be selected if they have a boundary that touches a selecting feature. When the inputs features are lines or polygons, the boundary of the input feature can only touch the boundary of the selecting feature, and no part of the input feature can cross the boundary of the selecting feature.
- SHARE_A_LINE_SEGMENT_WITH—The features in the input layer will be selected if they share a line segment with a selecting feature. The input and selecting features must be line or polygon.
- CROSSED_BY_THE_OUTLINE_OF—The features in the input layer will be selected if they are crossed by the outline of a selecting feature. The input and selecting features must be lines or polygons. If polygons are used for the input or selecting layer, the polygon's boundary (line) will be used. Lines that cross at a point will be selected, not lines that share a line segment.
- HAVE_THEIR_CENTER_IN—The features in the input layer will be selected if their center falls within a selecting feature. The center of the feature is calculated as follows: for polygon and multipoint, the geometry's centroid is used, and for line input, the geometry's midpoint is used.
3. Selecting Features (optional)
The features in the
input feature layer will be selected based on their relationship to the
features from this layer or feature class.
4. Search Distance (optional)
This parameter is only
valid if the Relationship parameter is set to one of the following:
WITHIN_A_DISTANCE_GEODESIC, WITHIN_A_DISTANCE, WITHIN_A_DISTANCE_3D, INTERSECT,
INTERSECT_3D, HAVE_THEIR_CENTER_IN, CONTAINS, or WITHIN.
If the
WITHIN_A_DISTANCE_GEODESIC option is used, a linear unit such as Kilometers or
Miles should be used.
5. Selection type (optional)
Determines how the selection will be applied to the input and how to combine with an existing selection. Note that there is no option here to clear an existing selection. To clear a selection, use the CLEAR_SELECTION option on the Select Layer By Attribute tool.
- NEW_SELECTION—The resulting selection replaces any existing selection. This is the default.
- ADD_TO_SELECTION—The resulting selection is added to an existing selection, if one exists. If no selection exists, this is the same as the NEW_SELECTION option.
- REMOVE_FROM_SELECTION—The resulting selection is removed from an existing selection. If no selection exists, the operation will have no effect.
- SUBSET_SELECTION—The resulting selection is combined with the existing selection. Only records that are common to both remain selected.
- SWITCH_SELECTION—Switches the selection. All records that were selected are removed from the selection, and all records that were not selected are added to the selection. The Selecting Features and Relationship parameters are ignored when this option is selected.
6. Invert Spatial Relationship (optional)
After the spatial relationship is evaluated, this option determines if the result should be used as is, or inverted. For example, this option can be used to quickly get a list of features that do not intersect or are not within a distance of features in another dataset.
- Unchecked—The result of the query will not be inverted. This is the default.
- Checked—The result of the query will be inverted. The inversion occurs before the selection is combined with existing selections.

Comments
Post a Comment