Multipatch and Point and Polygon to Raster Tools
Multipatch to Raster
How to use Multipatch to
Raster Tool in ArcToolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??Multipatch to Raster
Path to access the tool
:
Multipatch
to Raster Tool, To Raster Toolset, Conversion Toolbox
Multipatch to Raster
Converts multipatch
features to a raster dataset.
1. Input multipatch features
The input multipatch
features to be converted to a raster.
2. Output raster
The output raster
dataset to be created.
It will be of
floating-point type.
When not saving to a
geodatabase, specify .tif for a TIFF file format, .CRF for CRF file format,
.img for an ERDAS IMAGINE file format, or no extension for an Esri Grid raster
format.
3. Output cell size (optional)
The cell size for the
output raster being created.
This parameter can be
defined by a numeric value or obtained from an existing raster dataset. If the
cell size hasn’t been explicitly specified as the parameter value, then the
environment cell size value is used if specified;
otherwise some additional
rules are used to calculate it from the other inputs. See the usage for more
detail.
Point to Raster
How to use Point to Raster Tool in ArcToolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??Point to Raster
Path to access the tool
:
Point
to Raster Tool, To Raster Toolset, Conversion Toolbox
Point to Raster
Converts point features
to a raster dataset.
1. Input Features
The point or multipoint
input feature dataset to be converted to a raster.
2. Value field
The field used to assign
values to the output raster.
It can be any field of
the input feature dataset's attribute table.
If the Shape field of a
point or multipoint dataset contains z or m values, then either of these can be
used.
3. Output Raster Dataset
The output raster
dataset to be created.
When not saving to a
geodatabase, specify .tif for a TIFF file format, .CRF for CRF file format,
.img for an ERDAS IMAGINE file format, or no extension for an Esri Grid raster
format.
4. Cell assignment type (optional)
The method to determine
how the cell will be assigned a value when more than one feature falls within a
cell.
- MOST_FREQUENT—If there is more than one feature within the cell, the one with the most common attribute, in the Value field, is assigned to the cell. If they have the same number of common attributes, the one with the lowest FID is used.
- SUM—The sum of the attributes of all the points within the cell (not valid for string data).
- MEAN—The mean of the attributes of all the points within the cell (not valid for string data).
- STANDARD_DEVIATION—The standard deviation of attributes of all the points within the cell. If there are less than two points in the cell, the cell is assigned NoData (not valid for string data).
- MAXIMUM—The maximum value of the attributes of the points within the cell (not valid for string data).
- MINIMUM—The minimum value of the attributes of the points within the cell (not valid for string data).
- RANGE—The range of the attributes of the points within the cell (not valid for string data).
- COUNT—The number of points within the cell.
5. Priority field (optional)
This field is used when a feature should take preference over
another feature with the same attribute.
Priority field is only used with the MOST_FREQUENT cell assignment
type option.
6. Cell size (optional)
The cell size for the output raster being created.
This parameter can be defined by a numeric value or obtained from
an existing raster dataset. If the cell size hasn’t been explicitly specified
as the parameter value, then the environment cell size value is used if
specified; otherwise some additional rules are used to calculate it from the
other inputs. See the usage for more detail.
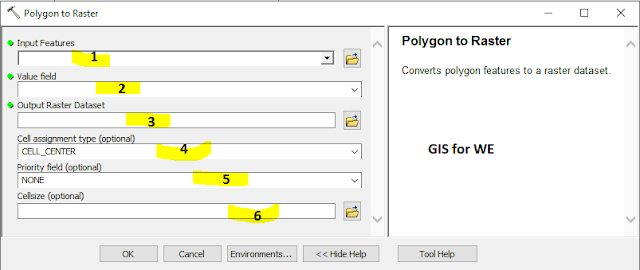
Polygon to Raster
How to use Polygon to
Raster Tool in ArcToolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??Polygon to Raster
Path to access the tool
:
Polygon
to Raster Tool, To Raster Toolset, Conversion Toolbox
Polygon to Raster
Converts polygon
features to a raster dataset.
1. Input Features
The polygon input
feature dataset to be converted to a raster.
2. Value field
The field used to assign
values to the output raster.
It can be any field of
the input feature dataset's attribute table.
3. Output Raster Dataset
The output raster
dataset to be created.
When not saving to a geodatabase,
specify .tif for a TIFF file format, .CRF for CRF file format, .img for an
ERDAS IMAGINE file format, or no extension for an Esri Grid raster format.
4. Cell assignment type (optional)
The method to determine
how the cell will be assigned a value when more than one feature falls within a
cell.
- CELL_CENTER—The polygon that overlaps the center of the cell yields the attribute to assign to the cell.
- MAXIMUM_AREA—The single feature with the largest area within the cell yields the attribute to assign to the cell.
- MAXIMUM_COMBINED_AREA—If there is more than one feature in a cell with the same value, the areas of these features will be combined. The combined feature with the largest area within the cell will determine the value to assign to the cell.
5. Priority field (optional)
This field is used to
determine which feature should take preference over another feature that falls over
a cell. When it is used, the feature with the largest positive priority is
always selected for conversion irrespective of the Cell assignment type chosen.
6. Cell size (optional)
The cell size for the
output raster being created.
This parameter can be defined by a numeric value or obtained from an existing raster dataset. If the cell size hasn’t been explicitly specified as the parameter value, then the environment cell size value is used if specified; otherwise some additional rules are used to calculate it from the other inputs. See the usage for more detail.



Comments
Post a Comment