Make Image Server Layer and LAS Dataset Layer and Mosaic Layer Tools
Make Image Server Layer
How to Make Image Server
Layer Tool in ArcToolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??
Make Image Server Layer
Path to access the tool
:
Make
Image Server Layer Tool, Layers
and Table Views Toolset, Data Management Tools
Toolbox
Make Image Server Layer
Creates a temporary
raster layer from an image service. The layer that is created will not persist
after the session ends unless the document is saved.
The input can also be a
SOAP URL to an image server.
1. Input Image Service
The name of the input
image service or the SOAP URL that references the image service. Browse to or
type the input image service. This tool can also accept a SOAP URL that
references the image service.
An example of using the
image service name called ProjectX is:
C:\MyProject\ServerConnection.ags\ProjectX.ImageServer.
An example of a URL is http://AGSServer:8399/arcgis/services/ISName/ImageServer.
2. Output Image Server Layer
The name of the output
image layer.
3. Expression (optional)
Using SQL, you can
define a query or use the Query Builder to build a query.
4. Template Extent (optional)
The output extent of the
image layer.
The output extent can be
specified by defining the four coordinates or by using the extent of an
existing layer.
5. Bands (optional)
Choose which bands to
export for the layer. If no bands are specified, all the bands will be used in
the output.
6. Output Cell Size (optional)
The cell size for the
output image service layer.
7. Processing Template (optional)
The raster function processing template that can be applied on the output image service layer.
- None—No processing template.
8. Mosaic Method (optional)
The mosaic method defines how the mosaic is created from different rasters.
- SEAMLINE—Smooth transitions between images using seamlines.
- NORTH_WEST—Display imagery that is closest to the northwest corner of the mosaic dataset boundary.
- CLOSEST_TO_CENTER—Display imagery that is closest to the center of the screen.
- LOCK_RASTER—Select specific raster datasets to display.
- BY_ATTRIBUTE—Display and prioritize imagery based on a field in the attribute table.
- CLOSEST_TO_NADIR—Display the rasters with viewing angles closest to zero.
- CLOSEST_TO_VIEWPOINT—Display imagery that is closest to a selected viewing angle.
- NONE—Order rasters based on the ObjectID in the mosaic dataset attribute table.
9. Order Field (optional)
The default field to use
to order the rasters when the mosaic method is By_Attribute. The list of fields
is defined as those in the service table that are of type metadata and are
integer (for example, the values can represent dates or cloud cover
percentage).
10. Order Base Value (optional)
The images are sorted
based on the difference between this input value and the attribute value in the
specified field.
11. Lock Raster ID (optional)
The raster ID or raster
name to which the service should be locked, such that only the specified
rasters are displayed. If left blank (undefined), it will be similar to the
system default. Multiple IDs can be defined as a semicolon-delimited list.
Make LAS Dataset Layer
How to Make LAS Dataset
Layer Tool in ArcToolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??
Make LAS Dataset Layer
Path to access the tool
:
Make
LAS Dataset Layer Tool, Layers and Table Views Toolset, Data Management Tools Toolbox
Make LAS Dataset Layer
Creates a LAS dataset
layer that can apply filters to LAS points and control the enforcement of
surface constraint features.
1. Input LAS Dataset
The LAS dataset to
process.
2. Output Layer
The name of the
resulting LAS dataset layer. Any backslash or forward slash can be used to
denote a group layer.
3. Class Codes (optional)
Allows the filtering of
LAS points by classification codes. The range of valid values will depend on
the class codes supported by the version of LAS files referenced by the LAS
dataset. All class codes will be selected by default.
- 0—Never processed by a classification method
- 1—Processed by a classification method but could not be determined
- 2—Bare earth measurements
- 3—Vegetation whose height is considered to be low for the area
- 4—Vegetation whose height is considered to be intermediate for the area
- 5—Vegetation whose height is considered to be high for the area
- 6—Structure with roof and walls
- 7—Erroneous or undesirable data that is closer to the ground
- 8—Reserved for later use, but used for model key points in LAS 1.1 - 1.3
- 9—Water
- 10—Railway tracks used by trains
- 11—Road surfaces
- 12—Reserved for later use, but used for overlap points in LAS 1.1 - 1.3
- 13—Shielding around electrical wires
- 14—Power lines
- 15—A lattice tower used to support an overhead power line
- 16—A mechanical assembly that joins an electrical circuit
- 17—The surface of a bridge
- 18—Erroneous or undesirable data that is far from the ground
- 19 - 63—Reserved class codes for ASPRS designation.
- 64 - 255—User-definable class codes.
4. Return Values (optional)
The return values to be used for filtering LAS points. When no value is specified, all returns are used.
- Last Return—Last return
- First of Many—First of many
- Last of Many—Last of many
- Single Return—Single return1—1st Return
- 2—2nd Return
- 3—3rd Return
- 4—4th Return
- 5—5th Return
- 6—6th Return
- 7—7th Return
- 8—8th Return
- 9—9th Return
- 10—10th Return
- 11—11th Return
- 12—12th Return
- 13—13th Return
- 14—14th Return
- 15—15th Return
5. Unflagged Points (optional)
Specifies whether data points that do not have any classification flags assigned should be enabled for display and analysis.
- Checked—Unflagged points will be displayed. This is the default.
- Unchecked—Unflagged points will not be displayed.
6. Synthetic Points (optional)
Specifies whether data points flagged as synthetic, or points that originated from a data source other than lidar, should be enabled for display and analysis..
- Checked—Synthetic points will be displayed. This is the default.
- Unchecked—Synthetic points will not be displayed.
7. Model Key-points (optional)
Specifies whether data points flagged as model key points, or significant measurements that should not be thinned away, should be enabled for display and analysis.
- Checked—Model key points will be displayed. This is the default.
- Unchecked—Model key points will not be displayed.
8. Withheld Points (optional)
Specifies whether data points flagged as withheld, which typically represent unwanted noise measurements, should be enabled for display and analysis.
- Unchecked—Withheld points will not be displayed. This is the default.
- Checked—Withheld points will be displayed.
9. Surface Constraints (optional)
The name of the surface constraint features that will be enabled in the layer. All constraints are enabled by default.
Make Mosaic Layer
How to Make Mosaic Layer Tool in ArcToolbox ArcMap ArcGIS??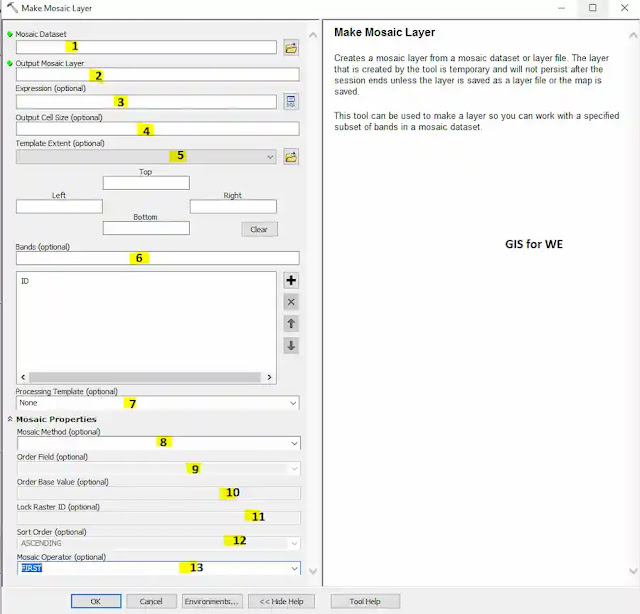
Make Mosaic Layer
Path to access the tool
:
Make
Mosaic Layer Tool, Layers and Table Views Toolset, Data Management Tools Toolbox
Make Mosaic Layer
Creates a mosaic layer
from a mosaic dataset or layer file. The layer that is created by the tool is
temporary and will not persist after the session ends unless the layer is saved
as a layer file or the map is saved.
This tool can be used to
make a layer so you can work with a specified subset of bands in a mosaic
dataset.
1. Mosaic Dataset
The path and name of the
input mosaic dataset.
2. Output Mosaic Layer
The name of the output
mosaic layer.
3. Expression (optional)
Using SQL, you can
define a query or use the Query Builder to build a query.
4. Output Cell Size (optional)
The cell size of the
output mosaic layer.
5. Template Extent (optional)
The output extent can be
specified by defining the four coordinates or by using the extent of an
existing layer.
6. Bands (optional)
Choose which bands to
export for the layer. If no bands are specified, all the bands will be used in
the output.
7. Processing Template (optional)
The raster function processing template that can be applied on the output mosaic layer.
- None—No processing template.
8. Mosaic Method (optional)
Choose the mosaic method. The mosaic method defines how the layer is created from different rasters in the mosaic dataset.
- CLOSEST_TO_CENTER—Sorts rasters based on an order where rasters that have their center closest to the view center are placed on top.
- NORTH_WEST—Sorts rasters based on an order where rasters that have their center closest to the northwest are placed on top.
- LOCK_RASTER—Enables a user to lock the display of single or multiple rasters, based on an ID or name. When you choose this option, you need to specify the Lock Raster ID.
- BY_ATTRIBUTE—Sorts rasters based on an attribute field and its difference from the base value. When this option is chosen, the order field and order base value parameters also need to be set.
- CLOSEST_TO_NADIR—Sorts rasters based on an order where rasters that have their nadir position closest to the view center are placed on top. The nadir point can be different from the center point, especially in oblique imagery.
- CLOSEST_TO_VIEWPOINT—Sorts rasters based on an order where the nadir position is closest to the user-defined viewpoint location and are placed on top.
- SEAMLINE—Cuts the rasters using the predefined seamline shape for each raster using optional feathering along the seams. The ordering is predefined during seamline generation. The LAST mosaic operator is not valid with this mosaic method.
9. Order Field (optional)
Choose the order field. When the mosaic method
is BY_ATTRIBUTE, the default field to use when ordering rasters needs to be
set. The list of fields is defined as those in the service table that are of
type metadata.
Choose the order field. When the mosaic method
is BY_ATTRIBUTE, the default field to use when ordering rasters needs to be
set. The list of fields is defined as those in the service table that are of
type metadata.
10. Order Base Value (optional)
The order base value.
The images are sorted based on the difference between this value and the
attribute value in the specified field.
11. Lock Raster ID (optional)
The Raster ID or raster
name to which the service should be locked so that only the specified rasters
are displayed. If left undefined, it will be similar to the system default.
Multiple IDs can be defined as a semicolon-delimited list.
12. Sort Order (optional)
Choose whether the sort order is ascending or descending.
- ASCENDING—The sort order will be ascending. This is the default.
- DESCENDING—The sort order will be descending.
13. Mosaic Operator (optional)
Choose the mosaic operator to use. When two or more rasters have the same sort priority, this parameter is used to further refine the sort order.
- FIRST—The first raster in the list will be on top. This is the default.
- LAST—The last raster in the list will be on top.
- MIN—The raster with the lowest value will be on top.
- MAX—The raster with the highest value will be on top.
- MEAN—The average pixel value will be on top.
- BLEND—The output cell value will be a blend of values; this blend value relies on an algorithm that is weight based and dependent on the distance from the pixel to the edge within the overlapping area.
- SUM—The output cell value will be the aggregate of all overlapping cells.

Comments
Post a Comment