Terrain to Points and Raster and TIN
Terrain to Points
How to use Terrain to Points Tool in Arc Toolbox ArcMap ArcGIS ??
 |
| Terrain to Points |
Terrain to Points Tool, From Terrain Toolset, Conversion Toolset, 3D Analyst
Toolbox
Terrain to Points
Converts a terrain
dataset into a new point or multipoint feature class.
1. Input Terrain
The terrain dataset to
process.
2. Output Feature Class
The feature class that
will be produced by this tool.
3. Pyramid Level Resolution (optional)
The z-tolerance or
window-size resolution of the terrain pyramid level that will be used by this
tool. The default is 0, or full resolution.
4. Input Embedded Feature Class (optional)
The name of the terrain
dataset's embedded points to be exported. If an embedded feature is specified,
only the points from the feature will be written to the output. Otherwise, all
points from all data sources in the terrain will be exported.
5. Output Feature Class Type (optional)
The geometry of the
output feature class.
·
MULTIPOINT—The output point features will be written to a
multipoint feature class. This is the default.
· POINT—The output point features will be written to a point feature class.
Terrain to Raster
How to use Terrain to Raster Tool in Arc Toolbox ArcMap ArcGIS ??
 |
| Terrain to Raster |
Terrain to Raster Tool, From Terrain Toolset, Conversion Toolset, 3D Analyst
Toolbox
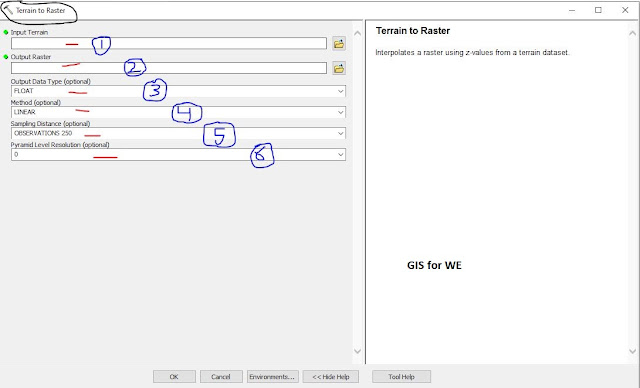
Terrain to Raster
Interpolates a raster
using z-values from a terrain dataset.
1. Input Terrain
The terrain dataset to
process.
2. Output Raster
The location and name of
the output raster. When storing a raster dataset in a geodatabase or in a folder
such as an Esri Grid, no file extension should be added to the name of the
raster dataset. A file extension can be provided to define the raster's format
when storing it in a folder, such as .tif to generate a GeoTIFF or .img to
generate an ERDAS IMAGINE format file.
If the raster is stored
as a TIFF file or in a geodatabase, its raster compression type and quality can
be specified using geoprocessing environment settings.
3. Output Data Type (optional)
Specifies the type of
numeric values stored in the output raster.
·
FLOAT—Output raster will use 32-bit floating point, which supports
values ranging from -3.402823466e+38 to 3.402823466e+38. This is the default.
·
INT—Output raster will use an appropriate integer bit depth. This
option will round z-values to the nearest whole number and write an integer to
each raster cell value.
4. Method (optional)
The interpolation method
that will be used to calculate cell values.
·
LINEAR—Applies a distance based weight to the Z of each node in
the triangle encompassing the center of a given cell, then sums the weighted
values to assign the cell value. This is the default.
·
NATURAL_NEIGHBORS—Applies an area based weighting scheme that uses
Voronoi polygons to determine cell values.
5. Sampling Distance (optional)
The sampling method and distance used to define
the cell size of the output raster.
6. Pyramid Level Resolution (optional)
The z-tolerance or
window-size resolution of the terrain pyramid level that will be used by this
tool. The default is 0, or full resolution.
Terrain to TIN
How to use Terrain to TIN Tool in Arc Toolbox ArcMap ArcGIS ??
 |
| Terrain to TIN |
Terrain to TIN Tool, From Terrain Toolset, Conversion Toolset, 3D Analyst
Toolbox
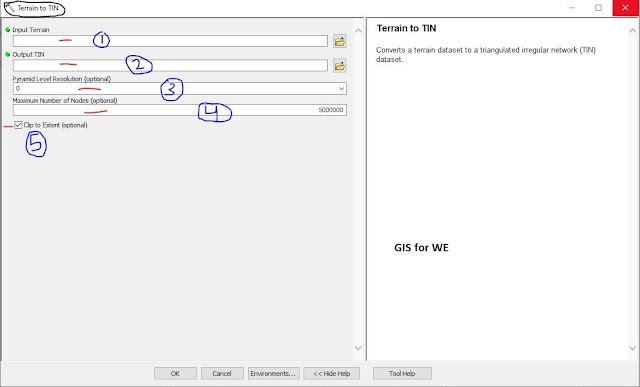
Terrain to TIN
Converts a terrain
dataset to a triangulated irregular network (TIN) dataset.
1. Input Terrain
The terrain dataset to
process.
2. Output TIN
The TIN dataset that
will be generated.
3. Pyramid Level Resolution (optional)
The z-tolerance or window-size resolution of the terrain pyramid level that will be used by this tool. The default is 0, or full resolution.
4. Maximum Number of Nodes (optional)
The maximum number of
nodes permitted in
the output TIN. The tool will return an error if the analysis extent and pyramid level would produce a TIN that exceeds this size. The default is 5 million.
5. Clip to Extent (optional)
Specifies whether the resulting TIN will be clipped against the
analysis extent. This only has an effect if the analysis extent is defined and
it's smaller than the extent of the input terrain.
·
Checked—Clips the output TIN against the analysis extent. This is
the default.
·
Unchecked—Does not clip the output TIN against the analysis
extent.

Comments
Post a Comment